Phytophotodermatitis
(Redirected from Berloque dermatitis)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Phytophotodermatitis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Lime disease, Berloque dermatitis, Margarita photodermatitis |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Skin inflammation, redness, blistering, hyperpigmentation |
| Complications | Hyperpigmentation, scarring |
| Onset | Minutes to hours after exposure |
| Duration | Days to weeks |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Contact with photosensitizing compounds and ultraviolet light exposure |
| Risks | Handling certain plants and fruits like limes, celery, parsley, figs |
| Diagnosis | Clinical diagnosis |
| Differential diagnosis | Contact dermatitis, sunburn, allergic reaction |
| Prevention | Avoidance of contact with photosensitizing substances, use of sunscreen |
| Treatment | Topical corticosteroids, cool compresses, analgesics |
| Medication | Corticosteroids, pain relievers |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | Common in certain occupational and recreational settings |
| Deaths | N/A |
Phytophotodermatitis: Cutaneous Reaction to Plants and Sunlight
Phytophotodermatitis, also known as berloque dermatitis or margarita photodermatitis, is a phototoxic inflammatory reaction of the skin. This condition occurs due to contact with certain plant substances followed by exposure to ultraviolet light, typically from the sun.
Definition and Mechanism
Phytophotodermatitis is caused by skin contact with photosensitizing compounds found in some plants and then exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays. The primary photosensitizing agents are furocoumarins, present in plants like limes, celery, and parsley.
Symptoms and Presentation
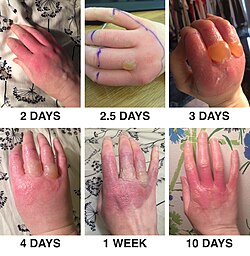
Typical symptoms include erythema (skin redness), edema (swelling), blisters (vesicles and bullae), and delayed hyperpigmentation. The severity of the reaction can vary, with some cases showing mild redness and others developing severe blistering.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of phytophotodermatitis include handling of the causative plants, especially under hot and moist conditions, and subsequent exposure to sunlight.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is often clinical, based on the characteristic appearance of the lesions and a history of potential exposure. Dermatologists may use patient history and skin examinations to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment and Management
Treatment involves managing symptoms, which may include topical steroids for inflammation and pain relief. Avoiding further exposure to sunlight can prevent exacerbation of the condition.
Prevention
Prevention strategies include wearing protective clothing and washing skin thoroughly after handling potential photosensitizing plants, followed by minimizing sun exposure.
Epidemiology
This condition can affect individuals of all ages but is more common in those frequently handling plants, such as gardeners and agricultural workers.
See Also
References
External Links
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


