File:Heterophyes LifeCycle.gif
From WikiMD's medical encyclopedia
Heterophyes_LifeCycle.gif (617 × 435 pixels, file size: 34 KB, MIME type: image/gif)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
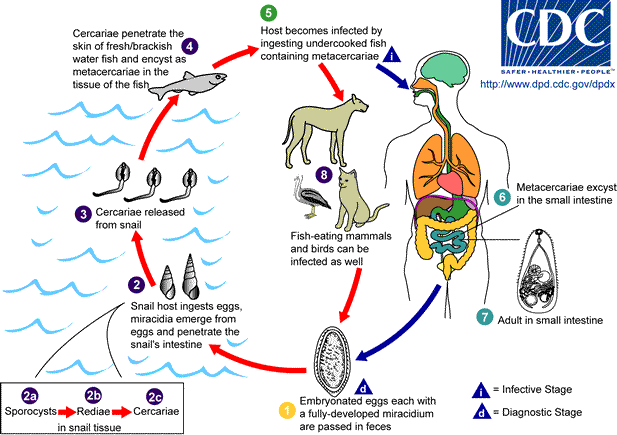
| current | 17:30, 18 October 2007 |  | 617 × 435 (34 KB) | Filip em | Adults release embryonated eggs each with a fully-developed miracidium, and eggs are passed in the host's feces . After ingestion by a suitable snail (first intermediate host), the eggs hatch and release miracidia which penetrate the snail’s intestine |
File usage
The following 3 pages use this file: