Hard palate
(Redirected from Hard Palate)
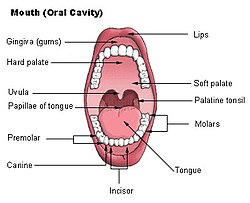
The hard palate is a partition between the nasal and oral cavities. Its anterior two-third is formed by the palatine processes of the maxillae and posterior one-third by the horizontal plates of the palatine bones.
The superior and inferior surfaces of the hard palate form the floor of the nasal cavity and the roof of the oral cavity, respectively.
- Anterolaterally, the hard palate becomes continuous with the alveolar arches and gums.
- The posterior margin of the hard palate is free and provides attachment to the soft palate.
The inferior surface of the hard palate presents the following features:
- Incisive fossa, a small pit anteriorly in the midline behind the incisor teeth, into which open the incisive canals. Each incisive canal/foramen (right and left) pierces the corresponding side and ascend into the corresponding nasal cavity. The incisive foramen transmits terminal parts of the nasopalatine nerve and greater palatine vessels.
- Greater palatine foramen, one on each side, lies in the posterolateral corner of the hard palate medial to the last molar tooth. It transmits the greater palatine nerve and vessels.
- Lesser palatine foramina (1–3 in number) on each side are in the pyramidal process of palatine bone and are located just behind the greater palatine foramen. They provide passage to lesser palatine nerve and vessels.
- Posterior nasal spine is a conical projection in the median plane on the sharp free posterior border of the hard palate.
- Palatine crest is a curved ridge near the posterior border of the hard palate.
- Masticatory mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the hard palate. In the anterior part, it is firmly united with the periosteum by multiple fibrous strands (Sharpey’s fibres), hence moving bolus of food does not displace the mucous membrane. It presents:
- transverse masticatory ridges on either side of midline, and
- palatine raphe, a narrow ridge of mucous membrane extending anteroposteriorly in the midline from a little papilla overlying the incisive fossa.
The hard palate is lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.
Arterial Supply
This is by greater palatine arteries from the third part of the maxillary artery. Each artery emerges from greater palatine foramen and passes forwards around the palate (lateral to the nerve) to enter the incisive canal and pass up into the nose.
Venous Drainage
The veins of hard palate drain into the pterygoid venous plexus (mainly) and pharyngeal venous plexus.
Nerve Supply
The hard palate is supplied by greater palatine and nasopalatine nerves derived from pterygopalatine ganglion. The greater palatine nerve supplies whole of the palate except anterior part of palate behind incisor teeth (the area of premaxilla), which is supplied by nasopalatine nerves.
Lymphatic Drainage
The lymphatics from palate drain mostly into the upper deep cervical lymph nodes and few into retropharyngeal lymph nodes.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD