Melnick–Needles syndrome
(Redirected from Melnick-Needles syndrome)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Melnick–Needles syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | MNS |
| Pronounce | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | Skeletal dysplasia, craniofacial dysmorphism, hearing loss |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
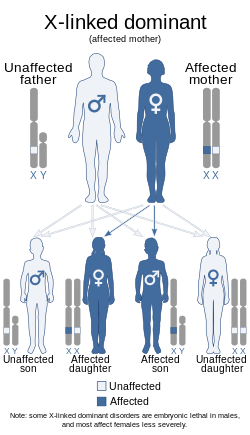
| Causes | Mutations in the FLNA gene |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Osteogenesis imperfecta, frontometaphyseal dysplasia |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Symptomatic treatment, orthopedic surgery |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on severity |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | |
Melnick–Needles syndrome (MNS) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by distinctive skeletal abnormalities and other physical features. It was first described in 1966 by American physicians Joel Melnick and Robert Needles.
Etymology
The syndrome is named after the physicians Joel Melnick and Robert Needles who first described the condition in 1966.
Signs and Symptoms
People with Melnick–Needles syndrome often have a characteristic facial appearance that includes a prominent forehead (frontal bossing), widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), full cheeks, and a pointed chin. Other features can include hearing loss, eye abnormalities, and respiratory problems.
Causes
Melnick–Needles syndrome is caused by mutations in the FLNA gene. This gene provides instructions for making a protein called filamin A, which helps build the network of protein filaments (cytoskeleton) that gives structure to cells and allows them to change shape and move.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Melnick–Needles syndrome is based on the presence of characteristic signs and symptoms. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment of Melnick–Needles syndrome is symptomatic and supportive. It may include physical therapy, surgery to correct bone abnormalities, and regular monitoring for potential complications.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with Melnick–Needles syndrome varies. Some individuals have a normal lifespan, while others may have life-threatening complications.
Epidemiology
Melnick–Needles syndrome is a rare disorder. The exact prevalence is unknown.
See Also
References
External Links
- Melnick-Needles syndrome on Genetics Home Reference
- Melnick-Needles syndrome on National Organization for Rare Disorders
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

