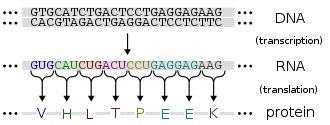Protein production
(Redirected from Recombinant protein)
Protein production is a complex biological process that involves the synthesis of proteins, which are essential molecules for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs. Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids and play a critical role in many biological processes, including enzyme catalysis, DNA replication, and the transport of molecules. The process of protein production is fundamental to cell biology, molecular biology, and biotechnology, and it has significant applications in medicine, pharmacology, and industrial biotechnology.
Overview
Protein production in cells involves two main processes: transcription and translation. During transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied to make an RNA molecule, specifically messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA then serves as a template for translation, where the ribosome reads the mRNA sequence and assembles the corresponding amino acids to form a protein. This process is tightly regulated and involves various cellular machinery and signaling pathways to ensure proteins are produced at the right time, place, and in the correct amounts.
Applications
The knowledge and manipulation of protein production have numerous applications:
Biopharmaceuticals
The production of therapeutic proteins and antibodies for use in treating diseases. Techniques such as recombinant DNA technology allow for the production of human proteins in microorganisms or cell cultures, which are then purified and used as drugs.
Industrial Enzymes
Enzymes produced through recombinant DNA technology are used in various industries, including the manufacture of biofuels, food processing, and waste management.
Research
Understanding protein production is crucial for biological research, enabling the study of protein function, protein-protein interactions, and the development of new biological assays and diagnostic tests.
Challenges
Despite its vast potential, protein production faces several challenges, including the high cost of production and purification, the stability and folding of recombinant proteins, and the potential for immune reactions in therapeutic applications.
Future Directions
Advancements in genetic engineering, synthetic biology, and nanotechnology hold promise for overcoming current limitations and expanding the possibilities of protein production. These include more efficient production systems, the design of novel proteins with enhanced functions, and the development of personalized medicine based on individual protein profiles.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD