Intravaginal administration
(Redirected from Vaginal administration)
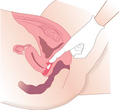
Intravaginal administration is a route of administration where the substance is applied inside the vagina. Medications using this route are administered in various forms, including creams, tablets, suppositories, or rings. This method is commonly used for its targeted effect at the site of application, reduced systemic side effects, and for its ease of use.
Indications
Intravaginal administration is indicated for several medical conditions and purposes, including:
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Especially in postmenopausal women, to relieve symptoms of vaginal atrophy, such as dryness, itching, and burning.
- Contraception: Certain contraceptive devices, like the vaginal ring, release hormones locally to prevent pregnancy.
- Treatment of vaginal infections and yeast infections: Antifungal and antibiotic medications can be applied directly to the affected area.
- Labor induction: Prostaglandins, in the form of gels or inserts, can be used to ripen the cervix and induce labor.
Advantages
The intravaginal route offers several advantages over other forms of medication administration:
- Direct delivery to the affected area allows for lower doses of medication, reducing the risk of systemic side effects.
- Bypasses the gastrointestinal tract, avoiding gastrointestinal side effects and degradation of the medication by stomach acid.
- Provides a convenient alternative for those who have difficulty swallowing pills.
Disadvantages
Despite its benefits, intravaginal administration may have disadvantages:
- Limited to female patients.
- Potential for local irritation or discomfort.
- Requires patient comfort and familiarity with the method of administration.
Types of Intravaginal Administration Forms
- Creams and Gels: Often used for hormonal therapies and to treat infections.
- Tablets: Typically used for yeast infections and contraceptive purposes.
- Suppositories: Solid forms that melt at body temperature, used for various treatments including hormonal therapy and infections.
- Vaginal Rings: Flexible rings that release medication over a prolonged period, used for contraception and HRT.
Procedure
The procedure for intravaginal administration varies depending on the form of medication but generally involves the following steps:
1. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water. 2. Remove the medication from its packaging. 3. Assume a comfortable position that allows for easy access to the vagina, such as squatting or lying on one's back with knees bent. 4. Gently insert the medication into the vagina as far as it will comfortably go, following the specific instructions provided with the medication. 5. Wash hands again after administration.
Conclusion
Intravaginal administration is a valuable route for delivering medications directly to the site of action in the female reproductive system. It offers the advantage of localized treatment with minimal systemic absorption, making it an effective and convenient option for various medical conditions. However, patient education and comfort with the method are essential for its success.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD