Abacus
Abacus
The abacus is a calculating tool that has been used since ancient times. It consists of a frame with rods, on which beads are moved to perform arithmetic calculations. The abacus is still used today in some parts of the world, particularly in Asia, for teaching arithmetic to children and for practical calculations.
History
The abacus has a long history, with its origins tracing back to ancient civilizations. The earliest known abacus was used by the Sumerians and later by the Babylonians. The device evolved over time, with different cultures developing their own versions.
Ancient Abacuses
The Salamis Tablet, dating back to around 300 BC, is one of the earliest known counting boards. It was used by the Greeks and is considered a precursor to the modern abacus.
Roman Abacus
The Romans developed their own version of the abacus, which was a portable device made of metal or wood. It was used for calculations in commerce and engineering.
Chinese Abacus
The Chinese abacus, known as the suanpan, was developed around the 2nd century BC. It typically has two beads on the upper deck and five beads on the lower deck, allowing for complex calculations.
Japanese Abacus
The Japanese abacus, or soroban, is a simplified version of the Chinese abacus. It has one bead on the upper deck and four beads on the lower deck, and is still used in Japan today.
Variants
Quipu
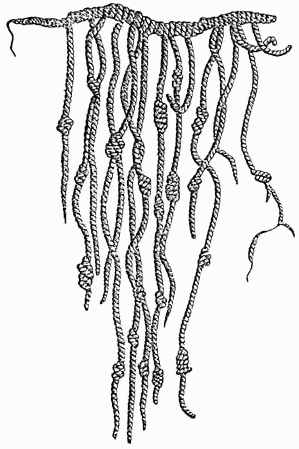
The quipu was used by the Inca Empire as a recording device. It consisted of colored threads and knots, and while not an abacus in the traditional sense, it served a similar purpose in keeping numerical records.
Yupana
The yupana was another calculating device used by the Incas. It was a grid-like structure used for arithmetic operations.
Russian Abacus
The Russian abacus, or schoty, is a single-deck abacus used in Russia. It is still used in some shops and markets for quick calculations.
European Abacus
The European abacus, or Kugleramme, was used in medieval Europe. It was similar to the Roman abacus but adapted for the decimal system.
Modern Use
The abacus is still used in some parts of the world, particularly in Asia, for teaching arithmetic to children. It is valued for its ability to enhance mental calculation skills and improve concentration.
Related Pages
Gallery
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD