Abdominal trauma
| Abdominal trauma | |
|---|---|
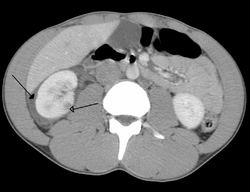
| |
| Synonyms | Abdominal injury |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, tenderness, bruising, rigidity |
| Complications | Internal bleeding, organ damage, peritonitis |
| Onset | Sudden, following trauma |
| Duration | Variable, depending on severity |
| Types | Blunt trauma, penetrating trauma |
| Causes | Motor vehicle collision, falls, assault, sports injuries |
| Risks | High-speed impact, violence, occupational hazards |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, imaging studies (CT scan, ultrasound) |
| Differential diagnosis | Appendicitis, pancreatitis, gastroenteritis |
| Prevention | Seat belts, protective gear, safety regulations |
| Treatment | Surgery, observation, fluid resuscitation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity and promptness of treatment |
| Frequency | Common in trauma centers |
| Deaths | N/A |
Gallery
- Pneumoperitoneum X-ray.jpg
X-ray showing pneumoperitoneum
Abdominal trauma refers to an injury to the abdomen. It can be classified as either blunt trauma or penetrating trauma. Abdominal trauma can involve damage to the abdominal wall, the abdominal cavity, or the retroperitoneal space.
Classification
Abdominal trauma is classified into two main types:
Blunt abdominal trauma
Blunt abdominal trauma is caused by a direct impact to the abdomen, such as from a car accident, fall, or assault. It is the most common type of abdominal trauma and can result in injury to solid organs like the liver, spleen, and kidneys.
Penetrating abdominal trauma
Penetrating abdominal trauma occurs when an object pierces the abdominal wall, such as a knife or bullet. This type of trauma can cause damage to both solid and hollow organs, leading to complications like peritonitis or hemorrhage.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of abdominal trauma can vary depending on the severity and type of injury. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Tenderness
- Bruising or swelling
- Nausea and vomiting
- Signs of shock
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of abdominal trauma typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Ultrasound: Often used in the form of a Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (FAST) exam to quickly assess for internal bleeding.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: Provides detailed images of the abdominal organs and can help identify injuries such as liver lacerations or kidney hematomas.
- X-ray: Can be used to detect free air in the abdomen, indicating a perforated organ.
Management
The management of abdominal trauma depends on the type and severity of the injury. Treatment options include:
- Observation: Minor injuries may only require monitoring and supportive care.
- Surgical intervention: Severe injuries, especially those involving major bleeding or organ perforation, may require laparotomy or other surgical procedures.
- Non-operative management: Some injuries, such as certain liver or spleen lacerations, can be managed without surgery through careful monitoring and supportive care.
Complications
Complications from abdominal trauma can include:
Related pages
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD, Prabhudeva


