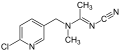
Acetamiprid
A neonicotinoid insecticide
| Chemical Compound | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider ID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | |
| Molar Mass | |
| Appearance | |
| Density | |
| Melting Point | |
| Boiling Point | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS Pictograms | [[File:|50px]] |
| GHS Signal Word | |
| GHS Hazard Statements | |
| NFPA 704 | [[File:|50px]] |
| References | |
Acetamiprid is a neonicotinoid insecticide that is used to control a variety of insect pests. It is particularly effective against aphids, whiteflies, and thrips. Acetamiprid is known for its systemic action, which allows it to be absorbed by plants and transported throughout their tissues, providing protection against pests that feed on the plant.
Chemical properties
Acetamiprid is a member of the neonicotinoid class of insecticides, which are chemically similar to nicotine. The chemical structure of acetamiprid includes a chloropyridinyl group and an acetamidine group, which contribute to its insecticidal activity. It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in water and organic solvents.
Mode of action
Acetamiprid acts on the nervous system of insects by binding to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. This binding leads to the disruption of nerve signal transmission, causing paralysis and eventually death of the insect. The specificity of acetamiprid for insect receptors over mammalian receptors contributes to its safety profile for humans and other non-target organisms.
Uses
Acetamiprid is used in agriculture to protect crops such as cotton, vegetables, fruit trees, and ornamental plants from insect damage. It is applied as a foliar spray or soil treatment and is effective at low application rates. Its systemic properties make it particularly useful for controlling sucking insects that are difficult to reach with contact insecticides.
Environmental impact
As a neonicotinoid, acetamiprid has been scrutinized for its potential impact on pollinators, particularly bees. While it is considered less toxic to bees than some other neonicotinoids, there is ongoing research into its effects on bee populations and other beneficial insects. Acetamiprid is also subject to environmental regulations to minimize its impact on non-target species and ecosystems.
Safety
Acetamiprid is classified as slightly toxic to humans and other mammals. It has a relatively low acute toxicity, but exposure should still be minimized to prevent potential health effects. Personal protective equipment is recommended for individuals handling the chemical.
Related pages
Acetamiprid
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD