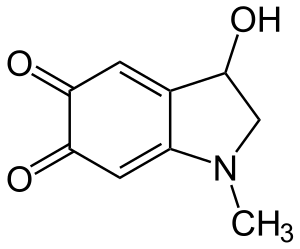
Adrenochrome
Adrenochrome is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C_9H_9NO_3, produced by the oxidation of adrenaline (epinephrine). The compound's name is derived from its origin in the adrenal glands and its chromatic properties.
Chemical Properties
Adrenochrome is a redox active compound that can be further oxidized to form adrenochrome monosemicarbazone or reduced to form leucoadrenochrome. It is known for its distinctive reddish color, which is a result of its chromophore structure.
Biological Role
Adrenochrome is not known to have any significant biological role in humans. It is a byproduct of the metabolism of adrenaline and is typically present in small amounts in the body. The compound has been studied for its potential effects on the central nervous system, but its physiological significance remains unclear.
Medical Research
Research into adrenochrome has explored its potential effects on mental health. Some studies have suggested that it may be linked to schizophrenia and other mental disorders, although these findings are controversial and not widely accepted in the medical community. The compound has also been investigated for its potential use in psychiatry and neurology.
Cultural References
Adrenochrome has been referenced in various works of literature and popular culture. It gained notoriety in the 1971 book Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas by Hunter S. Thompson, where it was depicted as a powerful hallucinogen. This portrayal, however, is fictional and not based on scientific evidence.
Synthesis
Adrenochrome can be synthesized in the laboratory through the oxidation of adrenaline. This process typically involves the use of oxidizing agents such as silver oxide or potassium permanganate.
Safety and Toxicity
The safety and toxicity of adrenochrome are not well-documented. It is not commonly used in medical practice, and its effects on human health are not fully understood. As with any chemical compound, proper handling and safety precautions should be observed.
See Also
References
External Links
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD