Allopathic medicine
Allopathic Medicine
Allopathic medicine, also known as biomedicine, conventional medicine, mainstream medicine, orthodox medicine, and Western medicine, is a system of healthcare practiced by medical doctors and other healthcare professionals. It involves treating symptoms and diseases using drugs, radiation, or surgery. Allopathic medicine is based on the application of the principles of the natural sciences, particularly biology and biochemistry, in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Historical Context
The term "allopathy" was coined in the 19th century by Samuel Hahnemann, the founder of homeopathy, to differentiate it from his system of homeopathic medicine. Allopathic medicine has evolved significantly since then, incorporating advances in medical research, technology, and pharmacology.
Principles and Methodologies
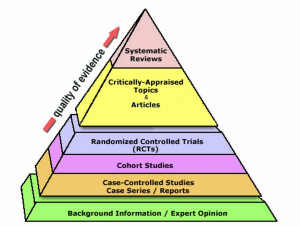
Allopathic medicine is characterized by a scientific approach to healthcare, emphasizing the diagnosis and treatment of illnesses through pharmacotherapy, surgical interventions, and radiation. It relies on evidence-based practices and clinical trials to inform treatment protocols.
- Pharmacotherapy: The use of pharmaceutical drugs to treat diseases.
- Surgery: The physical intervention, including incisions and manipulations, to treat injuries or disorders.
- Radiation Therapy: The use of ionizing radiation to treat cancer and other diseases.
Allopathic Medicine vs. Alternative Therapies
Allopathic medicine is often contrasted with alternative or complementary therapies, which may not always be grounded in scientific evidence. While allopathic medicine focuses on direct interventions to treat symptoms and diseases, alternative therapies may emphasize holistic approaches to patient care, including the mental, emotional, and spiritual health of patients.
Education and Training
Practitioners of allopathic medicine, such as physicians and surgeons, undergo extensive education and training. This typically includes completing a bachelor's degree, followed by a medical degree (MD), and residency training in a specialized field.
Role in Global Healthcare
Allopathic medicine plays a dominant role in the healthcare systems of most countries, providing the foundation for public health policies, medical education, and healthcare delivery.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its widespread acceptance and use, allopathic medicine faces challenges and criticisms, including the high cost of healthcare, the potential for overmedication and side effects, and the impersonal nature of some medical treatments.
See Also
References
- World Health Organization. (2021). Global Health Observatory data repository.
- National Institutes of Health. (2020). Understanding Allopathic Medicine.
External Links
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen