Alpha 2-antiplasmin
Alpha-2-antiplasmin is a serine protease inhibitor (serpin) that plays a crucial role in the regulation of the fibrinolytic system. It is primarily responsible for inhibiting plasmin, the enzyme that degrades fibrin clots. By controlling plasmin activity, alpha-2-antiplasmin helps maintain the balance between clot formation and clot dissolution, which is essential for normal hemostasis.
Structure and Function
Alpha-2-antiplasmin is a glycoprotein synthesized mainly in the liver. It circulates in the blood plasma and is composed of a single polypeptide chain. The primary function of alpha-2-antiplasmin is to inhibit plasmin, thereby preventing excessive fibrinolysis and ensuring that blood clots are stable enough to prevent bleeding.
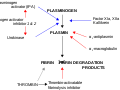
The interaction between alpha-2-antiplasmin and plasmin is a key component of the fibrinolytic system. When a blood clot forms, plasminogen is converted to plasmin, which then degrades fibrin. Alpha-2-antiplasmin binds to plasmin, inhibiting its activity and thus regulating the breakdown of fibrin clots.
Role in Fibrinolysis
Fibrinolysis is the process by which fibrin clots are broken down in the body. This process is essential for wound healing and the prevention of thrombosis. Alpha-2-antiplasmin is a major inhibitor of fibrinolysis, acting by binding to plasmin and preventing it from degrading fibrin.
In the fibrinolytic pathway, plasminogen is activated to plasmin by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) or urokinase. Plasmin then degrades fibrin into soluble fragments. Alpha-2-antiplasmin rapidly inhibits free plasmin, ensuring that fibrinolysis is localized to the site of the clot and does not lead to systemic bleeding.
Clinical Significance
Deficiencies or dysfunctions in alpha-2-antiplasmin can lead to bleeding disorders due to excessive fibrinolysis. Conversely, elevated levels of alpha-2-antiplasmin can contribute to thrombotic conditions by preventing the normal breakdown of clots.
Alpha-2-antiplasmin levels can be measured in the laboratory to assess fibrinolytic activity and diagnose bleeding disorders. Therapeutic modulation of alpha-2-antiplasmin activity is a potential strategy for managing conditions such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Related Pages
Alpha_2-antiplasmin
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD