Anal canal
Anal Canal
The anal canal is the terminal part of the large intestine that ends at the anus. It plays a crucial role in controlling the expulsion of feces from the body, a process regulated by a complex mechanism involving the anal sphincters and the rectum. Understanding the anatomy, function, and potential health issues related to the anal canal is essential for maintaining gastrointestinal health.
Anatomy
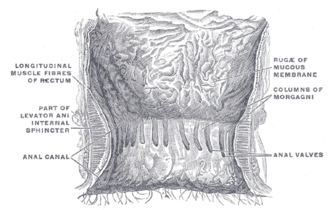
The anal canal is approximately 2.5 to 4 cm long, extending from the rectum to the anus. It is surrounded by two important muscles: the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter. The internal sphincter is made of smooth muscle and is under involuntary control, while the external sphincter consists of skeletal muscle and is under voluntary control.
The lining of the anal canal is specialized to suit its functions. The upper half is lined with mucous membrane that is continuous with the rectum, while the lower half is lined with skin-like squamous epithelium, making it more resistant to abrasion.
Function
The primary function of the anal canal is to control the expulsion of feces. This is achieved through the coordinated action of the anal sphincters and the rectal muscles. When feces enter the rectum, this triggers the urge to defecate. The internal anal sphincter relaxes involuntarily, but defecation only occurs if the external anal sphincter is voluntarily relaxed.
Health Issues
Several health issues can affect the anal canal, including:
- Anal fissures: Small tears in the lining of the anal canal, often caused by passing hard or large stools. - Hemorrhoids: Swollen blood vessels in and around the anus and lower rectum that can cause pain, itching, and bleeding. - Anal abscesses and fistulas: Infections in the anal glands that can lead to the formation of abscesses and, potentially, abnormal channels called fistulas. - Anal cancer: A rare form of cancer that affects the cells of the anal canal.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of anal canal issues often involves a physical examination, including inspection of the anal region, digital rectal examination, and possibly endoscopic procedures like anoscopy or colonoscopy. Treatment varies depending on the condition but may include dietary changes, medications, procedures to remove affected tissue, or, in some cases, surgery.
Prevention
Preventive measures for anal canal health include maintaining a high-fiber diet to prevent constipation and straining, practicing good hygiene in the anal area, and seeking prompt medical attention for any anal discomfort or irregularities.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD