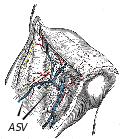
Anterior accessory saphenous vein
Anterior Accessory Saphenous Vein
The anterior accessory saphenous vein (AASV) is a significant superficial vein located in the lower limb. It is a variant of the saphenous vein system, which plays a crucial role in the venous drainage of the leg. Understanding the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of the AASV is essential for healthcare professionals, especially those involved in the diagnosis and treatment of venous disorders.
Anatomy
The AASV originates from the dorsal venous network of the foot and ascends anteriorly along the leg. It runs parallel to the great saphenous vein (GSV), but is located more superficially. The course of the AASV can vary significantly among individuals. Typically, it drains into the GSV, but it can also drain into the femoral vein or other superficial veins.
Function
The primary function of the AASV, similar to other superficial veins, is to return deoxygenated blood from the lower extremity back to the heart. It contains valves that prevent the backflow of blood, ensuring unidirectional flow towards the heart. The AASV, along with other veins in the saphenous system, plays a vital role in the venous return from the leg, especially during physical activities.
Clinical Significance
The AASV is of particular interest in the context of varicose veins and venous insufficiency. Varicose veins occur when the valves in the vein become weak or damaged, causing blood to pool and the vein to enlarge. The AASV, due to its superficial location and variable anatomy, is often involved in varicose vein pathology.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of AASV-related conditions typically involves a physical examination and imaging studies. Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that is commonly used to assess the anatomy and function of the AASV, helping to identify any reflux or obstruction.
Treatment
Treatment options for AASV-related varicose veins include conservative management, such as compression stockings, and procedural interventions. Minimally invasive techniques, such as sclerotherapy, radiofrequency ablation, and endovenous laser therapy, have become the preferred methods for treating varicose veins involving the AASV. In some cases, surgical removal of the affected vein may be necessary.
Conclusion
The anterior accessory saphenous vein is an important component of the venous system of the lower limb. Its role in venous return and its involvement in common venous disorders make it a significant subject of study in vascular medicine. Advances in diagnostic and treatment modalities have improved the management of conditions involving the AASV, leading to better patient outcomes.
Anterior_accessory_saphenous_vein
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD