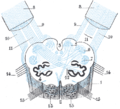
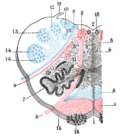
Anterior external arcuate fibers
Anterior External Arcuate Fibers
The anterior external arcuate fibers are a group of nerve fibers located in the brain. They are part of the white matter tracts that connect different regions of the brain, specifically the frontal and temporal lobes. In this article, we will explore the anatomy, function, and clinical significance of the anterior external arcuate fibers.
Anatomy
The anterior external arcuate fibers are located in the cerebral hemisphere, specifically in the white matter of the brain. They are part of the superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF), which is a bundle of nerve fibers that connects the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes.
The SLF can be divided into three major components: SLF I, SLF II, and SLF III. The anterior external arcuate fibers are a part of SLF III. They originate from the frontal lobe, specifically the prefrontal cortex, and extend towards the temporal lobe.
Function
The exact function of the anterior external arcuate fibers is not fully understood. However, studies suggest that they play a role in language processing and auditory integration. They are believed to be involved in the integration of auditory information with other cognitive processes, such as attention and memory.
The anterior external arcuate fibers are also thought to be involved in the control of eye movements. They connect the frontal eye fields, which are responsible for voluntary eye movements, with the temporal lobe, which is involved in visual processing.
Clinical Significance
Damage or disruption to the anterior external arcuate fibers can result in various neurological conditions. For example, lesions in this area have been associated with language disorders, such as aphasia. Patients with damage to these fibers may have difficulty understanding or producing language.
Additionally, abnormalities in the anterior external arcuate fibers have been observed in individuals with schizophrenia. This suggests a potential role of these fibers in the pathophysiology of the disorder.
Conclusion
The anterior external arcuate fibers are an important component of the white matter tracts in the brain. They connect the frontal and temporal lobes and are involved in language processing, auditory integration, and eye movement control. Understanding the anatomy and function of these fibers can provide valuable insights into various neurological conditions and contribute to the development of targeted therapies.
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD