Arctostaphylos uva-ursi
Series of six paired embryological vascular structures
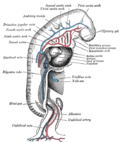
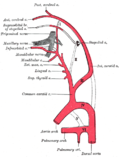
The aortic arches are a series of six paired embryological vascular structures that give rise to several major arteries in the adult. These arches are part of the pharyngeal arches and are crucial in the development of the circulatory system in vertebrates. In humans, these structures are transient and undergo significant remodeling to form the great arteries of the heart.
Development
The aortic arches develop from the aortic sac, which is an extension of the truncus arteriosus. Each arch is associated with a corresponding pharyngeal arch and is initially symmetrical on both sides of the embryo. As development progresses, these arches undergo complex transformations, with some regressing and others forming the major arteries of the body.
First Aortic Arch
The first aortic arch largely regresses, but it contributes to the formation of the maxillary artery, which supplies the deep structures of the face.
Second Aortic Arch
The second aortic arch also regresses significantly, with remnants forming the stapedial artery in the embryo, which is not present in adults.
Third Aortic Arch
The third aortic arch is crucial as it forms the common carotid arteries and the proximal portion of the internal carotid arteries.
Fourth Aortic Arch
The fourth aortic arch has different fates on the left and right sides. On the left, it forms part of the aortic arch itself, while on the right, it contributes to the formation of the right subclavian artery.
Fifth Aortic Arch
The fifth aortic arch is either rudimentary or absent in humans and does not contribute to any major adult structures.
Sixth Aortic Arch
The sixth aortic arch is also known as the pulmonary arch. On the left side, it forms the ductus arteriosus and part of the pulmonary arteries. On the right side, it contributes to the formation of the right pulmonary artery.
Clinical Significance
Abnormal development of the aortic arches can lead to congenital anomalies such as coarctation of the aorta, interrupted aortic arch, and vascular rings. These conditions can have significant clinical implications, often requiring surgical intervention.
Related pages
Gallery
Arctostaphylos uva-ursi
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD