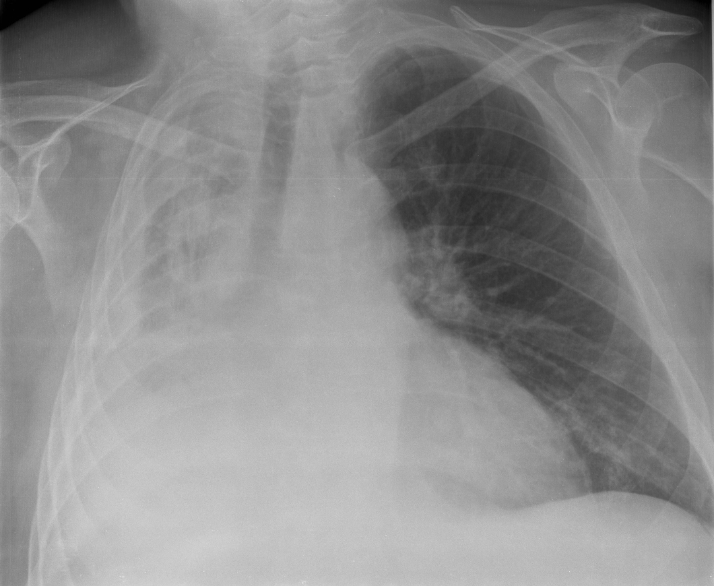
Atelectasis
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Atelectasis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Collapsed lung |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Difficulty breathing, cough, chest pain |
| Complications | Pneumonia, respiratory failure |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Obstruction of the airways, compression of the lung |
| Risks | Surgery, smoking, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| Diagnosis | Chest X-ray, CT scan, bronchoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Pneumonia, pleural effusion, pneumothorax |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Chest physiotherapy, bronchoscopy, surgery |
| Medication | Bronchodilators, antibiotics |
| Prognosis | Generally good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common, especially in hospitalized patients |
| Deaths | N/A |
Atelectasis refers to the partial or complete collapse of a lung, resulting from the failure of the lung tissue to fully expand. It could be caused by various factors including blocked airways due to a tumor, mucus, or foreign objects; infections such as pneumonia; lung diseases; prolonged bedrest with inadequate breathing; or effects of general anesthesia. The condition, in some cases, is also referred to as a collapsed lung.
Risk Factors
The risk of atelectasis can increase with certain factors or conditions. For instance, premature infants with undeveloped lungs may experience atelectasis due to respiratory distress syndrome. Other risk factors include smoking, obesity, sleep apnea, or underlying lung diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or cystic fibrosis. The condition is also more likely to occur post-surgery due to the impact of anesthetics on lung function, or because pain can inhibit deep breathing. To mitigate the risk of atelectasis during and after surgery, medical professionals may suggest quitting smoking, engaging in breathing exercises, administering certain medications, or employing breathing devices like a CPAP machine.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Atelectasis may remain asymptomatic if it only involves a small section of the lung. However, if a large portion of the lung is affected, symptoms such as fever, shallow breathing, wheezing, or coughing may manifest. Diagnosis usually involves a chest X-ray, which is the most common method employed. Additional confirmatory tests can include a bronchoscopy or other imaging techniques.
Treatment and Complications
Treatment of atelectasis primarily focuses on re-expanding the collapsed lung tissue. This could involve breathing or coughing exercises, inhaled medications, the use of breathing devices, or in severe cases, surgery. Generally, atelectasis tends to improve with time or appropriate treatment. Nevertheless, if it goes undiagnosed or untreated, it can lead to serious complications like fluid accumulation in the lungs, pneumonia, and even respiratory failure.
References
External links
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


