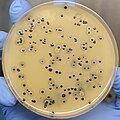
Baird-Parker agar
Baird-Parker Agar
Baird-Parker Agar is a selective culture medium primarily used for the isolation and enumeration of coagulase-positive staphylococci, particularly *Staphylococcus aureus*, from food, clinical, and environmental samples. This medium is named after the microbiologists Baird and Parker, who developed it in 1962.
Composition
Baird-Parker Agar contains several key components that make it selective and differential:
- Tryptone and Beef Extract: Provide essential nutrients and growth factors for bacterial growth.
- Yeast Extract: Supplies vitamins and additional growth factors.
- Sodium Pyruvate: Enhances the recovery of stressed cells and improves the growth of staphylococci.
- Glycine: Inhibits the growth of competing bacteria.
- Lithium Chloride: Acts as a selective agent against non-staphylococcal organisms.
- Egg Yolk Emulsion: Provides lecithin and lipids, which are hydrolyzed by lecithinase-positive staphylococci, resulting in a clear zone around colonies.
- Potassium Tellurite: Inhibits most gram-negative bacteria and some gram-positive bacteria, while allowing the growth of *Staphylococcus aureus*, which reduces tellurite to tellurium, forming black colonies.
Mechanism of Action
Baird-Parker Agar is both selective and differential. The selectivity is achieved through the use of lithium chloride and potassium tellurite, which suppress the growth of most non-staphylococcal bacteria. The differential aspect is due to the egg yolk emulsion, which allows the detection of lecithinase activity. Colonies of *Staphylococcus aureus* appear as black or gray due to tellurite reduction, often surrounded by a clear zone of egg yolk precipitation.
Procedure
1. Sample Preparation: Prepare the sample by homogenizing it in a suitable diluent. 2. Inoculation: Spread the sample onto the surface of the Baird-Parker Agar plate. 3. Incubation: Incubate the plates at 35-37°C for 24-48 hours. 4. Examination: Examine the plates for characteristic black colonies with clear zones.
Interpretation
- Positive Result: Black colonies with clear zones indicate the presence of coagulase-positive staphylococci, such as *Staphylococcus aureus*.
- Negative Result: Absence of black colonies or presence of colonies without clear zones suggests the absence of coagulase-positive staphylococci.
Applications
Baird-Parker Agar is widely used in:
- Food Microbiology: To test for contamination by *Staphylococcus aureus* in food products.
- Clinical Diagnostics: To isolate *Staphylococcus aureus* from clinical specimens.
- Environmental Monitoring: To assess the presence of staphylococci in environmental samples.
Limitations
While Baird-Parker Agar is effective for isolating *Staphylococcus aureus*, it may not differentiate between all coagulase-positive staphylococci. Some strains may not produce the characteristic black colonies, and additional confirmatory tests, such as the coagulase test, may be necessary.
Also see
| Microbiology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This microbiology related article is a stub.
|
Baird-Parker agar gallery
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD