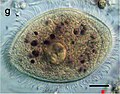
Balantidium coli
Balantidium coli is a protozoan parasite responsible for causing the disease balantidiasis, a primarily intestinal infection that can occasionally become systemic. This organism is notable for being the largest protozoan parasite to infect humans and is unique among ciliates for its pathogenicity. Balantidium coli has a complex life cycle, alternating between trophozoite and cyst stages, facilitating its transmission and survival in various environments.
Life Cycle
The life cycle of Balantidium coli involves two distinct stages: the trophozoite and the cyst. The trophozoite is the active, motile stage, which resides in the host's large intestine, where it can cause disease. In contrast, the cyst is the infectious stage, excreted in the feces of an infected host and capable of surviving outside the host in a dormant state until ingested by another host.
- Trophozoite Stage: In this stage, B. coli trophozoites colonize the large intestine, adhering to the mucosal lining and feeding on intestinal bacteria and nutrients. They may cause lesions and ulcers through mechanical and enzymatic action, leading to dysentery-like symptoms.
- Cyst Stage: The trophozoites undergo encystation to form cysts, which are then excreted in the feces. These cysts are hardy and can survive in moist environments for weeks to months. Infection occurs when another host ingests these cysts through contaminated water or food.
Transmission
Transmission of Balantidium coli primarily occurs through the fecal-oral route, with humans and other mammals, particularly pigs, serving as reservoir hosts. Ingestion of contaminated water or food with fecal matter containing viable cysts is the most common mode of transmission. Poor sanitation and hygiene practices are significant risk factors for balantidiasis.
Symptoms and Treatment
Balantidiasis can range from asymptomatic to severe, with symptoms including watery diarrhea, abdominal pain, and, in extreme cases, perforation of the colon. The severity of the disease is influenced by the immune status of the host and the number of cysts ingested.
Treatment typically involves antibiotics, with tetracycline being the drug of choice. Other effective medications include metronidazole and iodoquinol. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and systemic spread of the infection.
Prevention
Preventive measures for balantidiasis focus on improving sanitation and hygiene to reduce fecal contamination of water and food. This includes:
- Safe handling and disposal of human and animal feces
- Ensuring access to clean drinking water
- Practicing good personal hygiene, such as regular handwashing
- Proper food preparation and storage
Epidemiology
Balantidium coli is distributed worldwide, with higher prevalence in tropical and subtropical regions where conditions favor its survival and transmission. It is more common in areas with poor sanitation and in populations with close contact with pigs, which are significant reservoir hosts.
See Also
Balantidium_coli
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD