Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, fought in 9 AD, was a pivotal conflict between the Roman Empire and Germanic tribes led by Arminius, a chieftain of the Cherusci. This battle took place in the Teutoburg Forest in what is now modern-day Germany. It marked a significant defeat for the Romans and is often cited as one of the greatest disasters in Roman military history. The battle had far-reaching consequences for the Roman expansion into Germania and is remembered as a major event in the history of Europe.
Background
The Roman Empire, under the leadership of Augustus, sought to expand its borders into the Germanic territories east of the Rhine River. Publius Quinctilius Varus, a Roman general, was tasked with the governance of the newly conquered Roman province of Germania. However, the Roman occupation faced resistance from the local Germanic tribes.
Arminius, who had received military training from the Romans and had served as an auxiliary in the Roman army, used his knowledge of Roman military tactics to unite various Germanic tribes against the Roman invaders. He devised a plan to lure the Roman legions into the Teutoburg Forest, where he planned to ambush them.
The Battle
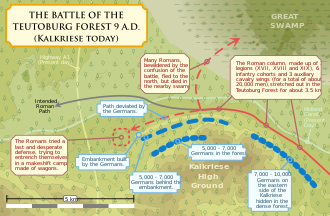
In the late summer of 9 AD, Varus led three Roman legions, along with auxiliary troops and cavalry, totaling around 20,000 men, into the Teutoburg Forest. Arminius, under the guise of an ally, led Varus and his legions into a trap. Heavy rain and difficult terrain slowed the Roman advance, making them vulnerable.
The Germanic tribes, familiar with the forest terrain, launched a series of surprise attacks on the stretched Roman column. The Romans, unable to form their traditional battle lines or utilize their superior military tactics effectively, were overwhelmed. The battle lasted for three days, with the Romans suffering heavy casualties. Varus, realizing the defeat was imminent, committed suicide. The annihilation of the three legions in the Teutoburg Forest was a devastating blow to Roman pride and military might.
Aftermath
The defeat at the Teutoburg Forest had significant implications for the Roman Empire. Augustus was reportedly so shaken by the loss that he would wander the palace, banging his head against the walls, and lamenting, "Quintilius Varus, give me back my legions!" The Roman Empire ceased its expansion into Germania, and the Rhine River became the de facto border between the Roman Empire and the Germanic tribes for the next few centuries.
The victory by the Germanic tribes under Arminius's leadership is celebrated in German history as the moment when Germanic independence was preserved against Roman conquest. However, Arminius's victory also led to internal conflicts among the Germanic tribes, and he was eventually killed in AD 21.
Legacy
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest has been romanticized in German nationalism and is often portrayed as a symbol of German unity and strength. It also serves as a cautionary tale about military overreach and the importance of understanding local conditions and enemy tactics.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD