Big Bang
The Big Bang is the prevailing cosmological model explaining the origin of the Universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model describes how the Universe expanded from a very high-density and high-temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), and large-scale structure.
Overview
The term "Big Bang" was originally coined by Fred Hoyle during a 1949 radio broadcast, intended as a pejorative to describe the theory which posits that the Universe began as a small singularity, then inflated over the next 13.8 billion years to the cosmos that we know today. Despite its initial reception, the Big Bang theory has become the most widely accepted and supported explanation among the scientific community for the origin of the Universe.
Evidence
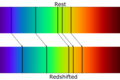
Several lines of evidence support the Big Bang theory. The most compelling include the observation of the redshift of galaxies, indicating that the Universe is expanding; the discovery of the Cosmic Microwave Background radiation, a relic of the early Universe; and the distribution of light elements, such as hydrogen and helium, which matches predictions from the Big Bang nucleosynthesis models.
Cosmic Microwave Background
The Cosmic Microwave Background is considered the afterglow radiation from the Big Bang, discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson. This discovery provided substantial evidence that the Universe had a hot and dense origin.
Galactic Redshift
Observations by Edwin Hubble in 1929 showed that galaxies are moving away from us in all directions, a phenomenon known as the Hubble expansion. This observation is a cornerstone of the Big Bang theory, indicating that the Universe itself is expanding.
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis
Big Bang nucleosynthesis refers to the production of light elements in the early stages of the Universe. The relative abundances of light elements such as hydrogen, helium, and lithium observed in the Universe match the predictions made by Big Bang nucleosynthesis models, providing strong evidence for the theory.
Theoretical Framework
The Big Bang theory is grounded in the equations of general relativity, with modifications that account for quantum mechanics at the singularity. The theory has evolved over time, incorporating new observations and measurements. One of the significant developments is the concept of inflation, a period of exponential expansion that is believed to have occurred in the first fractions of a second after the Big Bang.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the Big Bang theory is the most widely accepted model for the Universe's origin and evolution, it is not without its challenges. These include the horizon problem, the flatness problem, and the mystery of dark matter and Dark Energy. The theory of inflation was proposed to address some of these issues, but it also requires further empirical validation.
Ongoing and future observations, such as those from the James Webb Space Telescope and other advanced telescopes, promise to provide deeper insights into the early Universe, potentially offering more evidence in support of the Big Bang theory or leading to new theories altogether. Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
Big Bang
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD