Biginelli reaction
Biginelli Reaction
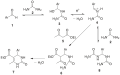
The Biginelli reaction is a significant chemical reaction that allows for the synthesis of dihydropyrimidinones (DHPMs), which are a class of heterocyclic compounds. This reaction was first reported in 1893 by Pietro Biginelli, an Italian chemist, hence its name. The Biginelli reaction is a multicomponent reaction (MCR), meaning it involves the simultaneous reaction of three or more starting materials to form a product, where the core structure is a 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one. The typical substrates for this reaction include an aldehyde, a β-keto ester (or a β-diketone), and urea or thiourea.
Reaction Mechanism
The mechanism of the Biginelli reaction involves several steps, starting with the formation of an enamine from the β-keto ester and the aldehyde. This enamine then reacts with urea or thiourea to form an intermediate, which undergoes cyclization to produce the dihydropyrimidinone core structure. The reaction is typically acid-catalyzed, with various acids being used to promote the reaction, including both organic and inorganic acids.
Variations and Developments
Over the years, several modifications and improvements have been made to the original Biginelli reaction protocol to increase its efficiency, yield, and scope. These include the use of different catalysts, such as Lewis acids, Brønsted acids, and even heterogeneous catalysts. Additionally, microwave-assisted and solvent-free conditions have been explored to enhance the reaction rates and environmental friendliness of the process.
Applications
Dihydropyrimidinones, the products of the Biginelli reaction, exhibit a wide range of biological activities, including antihypertensive, antiviral, and anticancer properties. This makes the Biginelli reaction an important tool in medicinal chemistry for the synthesis of new pharmaceuticals. Furthermore, the reaction is used in the synthesis of calcium channel blockers, a class of medications used to treat high blood pressure.
See Also
External Links
Biginelli reaction gallery
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD