Biogas
Biogas is a type of biofuel that is naturally produced from the decomposition of organic waste material. When organic matter, such as food scraps and animal waste, break down in an anaerobic environment (an environment absent of oxygen), they release a blend of gases, primarily methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with small amounts of other gases such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S). This gas mixture can be used as an energy source, making biogas a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Production
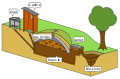
The production of biogas occurs in a system known as a biogas digester or anaerobic digester. These systems facilitate the anaerobic digestion process, which involves four key stages: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis. During these stages, microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The end product is biogas, a versatile energy source that can be used for heating, electricity generation, and as a fuel for vehicles.
Composition
Biogas primarily consists of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), with methane making up about 50-75% of the gas mixture. The high methane content is what gives biogas its energy potential. The exact composition of biogas can vary depending on the type of organic material used in the digestion process and the conditions within the digester.
Benefits
Biogas production offers several environmental and economic benefits. It provides a way to manage waste, reducing the need for landfill space and the emission of greenhouse gases from organic waste decomposition. Utilizing biogas as an energy source can also help reduce dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to energy security and reducing carbon footprints. Moreover, the by-product of biogas production, known as digestate, can be used as a nutrient-rich fertilizer, closing the loop in a sustainable waste-to-energy cycle.
Applications
Biogas can be used in various applications, including:
- Generating electricity
- Heating
- As a fuel for vehicles
- Upgrading to biomethane, a renewable natural gas substitute
Challenges
Despite its benefits, the adoption of biogas technology faces several challenges. These include the initial investment costs for digester systems, the need for a continuous supply of organic waste materials, and the management of impurities in the biogas. Additionally, the spread of biogas technology is limited by a lack of awareness and supportive policies in some regions.
Future Prospects
The future of biogas looks promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements aimed at improving the efficiency and reducing the costs of biogas production. Governments and organizations worldwide are beginning to recognize the potential of biogas in achieving renewable energy targets and mitigating climate change, leading to more supportive policies and incentives for biogas projects.
Biogas
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD