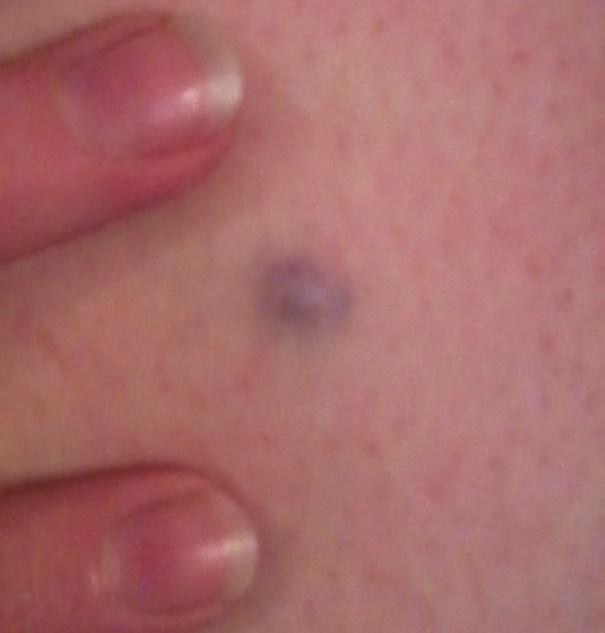
Blue nevus
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Blue nevus | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Nevus bleu |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Blue or blue-black skin lesion |
| Complications | Rarely, malignant transformation |
| Onset | Usually childhood or adolescence |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Proliferation of dermal melanocytes |
| Risks | Sun exposure, genetic predisposition |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, dermoscopy, biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Melanoma, dermatofibroma, hemangioma |
| Prevention | None specific |
| Treatment | Usually none required, surgical excision if necessary |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Excellent, benign condition |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Blue nevus (also known as blue nevomelanocytic nevus and nevus bleu) is a type of melanocytic nevus characterized by its distinct blue color. This coloration is due to the melanin pigment being deeper in the dermis, rather than in the epidermis, making the nevus appear blue due to the Tyndall effect. Blue nevi are generally benign, but on rare occasions, they can evolve into a melanoma, a type of skin cancer.
Etiology and Pathogenesis
The exact cause of blue nevi is not well understood, but they are believed to arise from the proliferation of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells) deep within the dermis. Unlike most nevi, which are located in the epidermis or at the epidermal-dermal junction, the melanocytes in blue nevi are found deeper in the skin. This positioning, combined with the scattering of light as it passes through the skin, results in the characteristic blue color.
Clinical Features
Blue nevi are typically small, round, and have a smooth surface. They can range in color from blue to blue-black or even gray. The size usually does not exceed a few millimeters in diameter, but larger lesions are possible. These nevi are most commonly found on the limbs, particularly the hands and feet, but can also appear on the face, buttocks, and sacral area.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a blue nevus is primarily clinical, based on its distinctive appearance. However, if there is any doubt or concern about the nature of the lesion, a dermatoscopy or a skin biopsy may be performed. Dermatoscopy can help differentiate a blue nevus from other pigmented lesions, while a biopsy and subsequent histological examination can confirm the diagnosis and rule out malignancy.
Treatment and Management
In most cases, blue nevi do not require treatment as they are benign and asymptomatic. However, if a blue nevus shows signs of change in size, shape, color, or becomes symptomatic (itching, bleeding), it should be evaluated by a dermatologist. Surgical removal may be recommended in these cases to exclude melanoma. Regular monitoring of the lesion is advised for individuals with blue nevi, especially if there is a personal or family history of melanoma.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with blue nevi is generally excellent, as these lesions are benign. However, there is a very low risk of transformation into melanoma. Therefore, awareness and monitoring of any changes in the nevus are important.
Epidemiology
Blue nevi are relatively uncommon and can occur in individuals of any age, but they are more frequently observed in adolescents and young adults. There is no significant gender predilection, and they can affect all skin types, although they may be less noticeable on darker skin.
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

