Breaststroke
Breaststroke is a swimming stroke that is swum on the chest, with the torso stationary and minimal rotation. It is one of the four swimming strokes used in competitive swimming, alongside the freestyle, backstroke, and butterfly stroke. The breaststroke is distinguished by its unique arm and leg movements, which occur in a simultaneous, symmetrical manner. This stroke is known for its technical precision and the timing required to perform it efficiently.
History
The origins of the breaststroke can be traced back to the Stone Age, making it the oldest of the competitive swimming strokes. Early depictions and descriptions suggest that human beings used a form of breaststroke to swim across rivers and lakes. The stroke has evolved significantly over the centuries, with major changes in technique occurring during the 20th century, which led to faster swimming times and new competitive standards.
Technique
The breaststroke consists of three main parts: the pull, the kick, and the glide. Each phase must be executed in harmony to maintain speed and efficiency in the water.
Pull
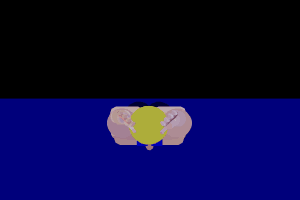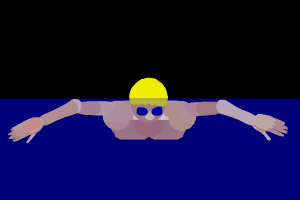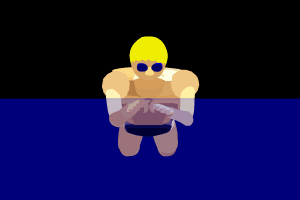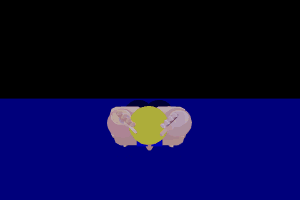
The pull phase begins with the swimmer's arms extended straight forward. The hands then sweep outwards and slightly downwards in a circular motion, ending with the hands pushing back towards the hips. This motion helps to propel the swimmer forward.
Kick
The kick, often referred to as the "frog kick," involves the swimmer's legs bending at the knees and then extending outward and backward. This movement provides additional propulsion and helps to maintain the swimmer's balance in the water.
Glide
After the pull and kick, the swimmer extends their arms forward and brings their legs together, assuming a streamlined position. This glide phase is crucial for maintaining momentum and preparing for the next stroke cycle.
Rules
In competitive swimming, breaststroke has specific rules that govern how the stroke must be performed. Swimmers must keep their body on their breast throughout the race; alternating movements of the arms and legs are required, and the hands must be pushed forward together from the breast on, under, or over the water. Turns and finishes require both hands to touch the wall simultaneously in the same horizontal plane.
Training and Technique Improvement
Improving breaststroke technique involves focused training on each part of the stroke, particularly the coordination of the pull, kick, and glide. Swimmers often use drills to isolate and improve specific aspects of their stroke, such as kick efficiency or arm movement precision.
In Competitive Swimming
Breaststroke is one of the strokes swum in medley events, both individually and in relays. It is the second stroke swum in the individual medley and the first in the medley relay. Due to its technical nature, mastering the breaststroke can be challenging but is essential for competitive swimmers who participate in medley events.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD