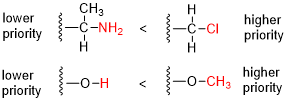Cahn–Ingold–Prelog priority rules
Cahn–Ingold–Prelog priority rules
The Cahn–Ingold–Prelog priority rules (CIP rules) are a set of rules used in organic chemistry to unambiguously name the stereoisomers of a molecule. These rules are named after the chemists Robert Sidney Cahn, Christopher Kelk Ingold, and Vladimir Prelog, who developed them.
Overview
The CIP rules are used to assign priorities to the substituents attached to a chiral center or a double bond. These priorities are then used to determine the absolute configuration (R or S) of chiral centers and the E-Z notation for double bonds.
Priority Assignment
The priority of substituents is determined based on the atomic number of the atoms directly attached to the chiral center or double bond. The higher the atomic number, the higher the priority. If two substituents have the same atomic number, the next atoms in the substituents are compared, and this process continues until a difference is found.
Steps for Assigning Priorities
1. Identify the chiral center or double bond: Locate the atom or bond in question. 2. Assign priorities based on atomic number: Compare the atomic numbers of the atoms directly attached to the chiral center or double bond. 3. Resolve ties by comparing subsequent atoms: If two substituents have the same atomic number, compare the next set of atoms in the substituents. 4. Consider multiple bonds: Treat multiple bonds as if the atoms were duplicated or triplicated.
Absolute Configuration (R/S)
Once the priorities of the substituents are assigned, the absolute configuration of a chiral center can be determined: 1. Orient the molecule so that the substituent with the lowest priority is pointing away from you. 2. Observe the sequence of the remaining three substituents. 3. If the sequence is clockwise, the configuration is R (rectus). 4. If the sequence is counterclockwise, the configuration is S (sinister).
E-Z Notation
For double bonds, the E-Z notation is used: 1. Assign priorities to the substituents on each carbon of the double bond. 2. If the highest priority substituents are on the same side of the double bond, the configuration is Z (zusammen). 3. If the highest priority substituents are on opposite sides, the configuration is E (entgegen).
Applications
The CIP rules are essential for the precise communication of the stereochemistry of molecules in chemical nomenclature. They are widely used in the fields of pharmacology, biochemistry, and materials science.
See Also
- Stereochemistry
- Chirality (chemistry)
- IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry
- Enantiomer
- Diastereomer
References
External Links
priority rules| |_}} {{#replace:Cahn–Ingold–Prelog priority rules| |_}}
.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD