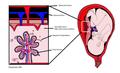
Cell-free fetal DNA
Cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) is fetal DNA that circulates freely in the maternal blood. It originates from the placenta and can be detected as early as the 5th week of pregnancy. The discovery of cffDNA has led to significant advancements in non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), allowing for the early detection of certain genetic conditions without the need for invasive procedures such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
Overview
Cell-free fetal DNA is released into the maternal bloodstream through the apoptosis of placental trophoblast cells. The concentration of cffDNA increases throughout pregnancy and rapidly declines after childbirth, disappearing from the maternal circulation within hours.
Clinical Applications
The primary application of cffDNA is in non-invasive prenatal testing. NIPT can screen for chromosomal abnormalities such as Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), and Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) with high accuracy. It can also be used to determine the Rh factor of the fetus, which is crucial in managing Rh incompatibility between the mother and fetus.
Advantages
- Non-invasive, posing no risk to the fetus
- High sensitivity and specificity for detecting certain chromosomal abnormalities
- Can be performed early in pregnancy
Limitations
- Not diagnostic; positive results require confirmation through invasive testing
- May not detect all genetic conditions or chromosomal abnormalities
Ethical Considerations
The use of cffDNA in prenatal testing raises ethical concerns, including the potential for early gender determination and the implications of detecting non-life-threatening genetic conditions. There is ongoing debate regarding the scope of testing and the management of incidental findings.
Future Directions
Research is ongoing to expand the range of conditions detectable through cffDNA analysis and to improve the accuracy of NIPT. Efforts are also being made to reduce the cost of testing, making it accessible to a broader population.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD