Central neurogenic hyperventilation
Central neurogenic hyperventilation (CNH) is a rare respiratory disorder characterized by a sustained pattern of rapid and deep breathing, resulting from brain dysfunction. Unlike other forms of hyperventilation, which can be voluntary or due to anxiety, CNH is driven by damage or malfunction within the central nervous system.
Causes
CNH is most commonly associated with severe brain injury, brainstem lesions, or neurological diseases that affect the brain's ability to regulate breathing. Conditions that have been linked to CNH include brain tumors, encephalitis, stroke, and traumatic brain injury. The exact mechanism by which these conditions lead to CNH is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the disruption of the neural pathways that control breathing.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of CNH is a pattern of rapid and deep breathing that is constant and does not vary with physical activity or sleep. This can lead to alkalosis, a condition in which the blood becomes too alkaline due to the excessive loss of carbon dioxide. Other symptoms may include difficulty in speaking, confusion, and a general deterioration in neurological function.
Diagnosis
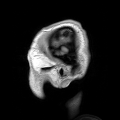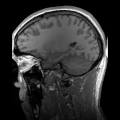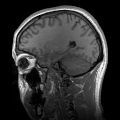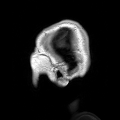
Diagnosis of CNH involves a thorough medical history and physical examination, along with diagnostic tests to assess respiratory function and identify potential underlying causes. Imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans of the brain may be used to detect abnormalities in the brainstem or other areas that could be causing the hyperventilation. Blood tests may also be conducted to measure levels of carbon dioxide and other gases in the blood.
Treatment
Treatment of CNH focuses on managing the underlying condition that is causing the hyperventilation. This may involve surgery to remove a brain tumor, medication to treat an infection, or other interventions aimed at reducing brain swelling and pressure. In some cases, breathing may need to be supported mechanically until the underlying condition can be addressed.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with CNH varies depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In some cases, treating the underlying condition can lead to a significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life. However, in cases where the damage to the brain is severe, the prognosis may be poor.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD