Chlorosulfolipid
Chlorosulfolipids are a unique class of organic compounds characterized by their structure containing chlorine, sulfur, and lipid elements. These compounds are primarily found in certain species of algae and have garnered attention due to their unusual chemical properties and potential biological activities. Chlorosulfolipids are notable for their complex molecular structures, which include multiple chlorine atoms, making them a subject of interest in the fields of organic chemistry and biochemistry.
Structure and Classification
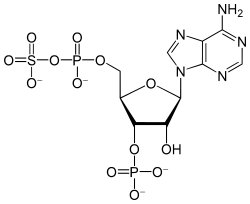
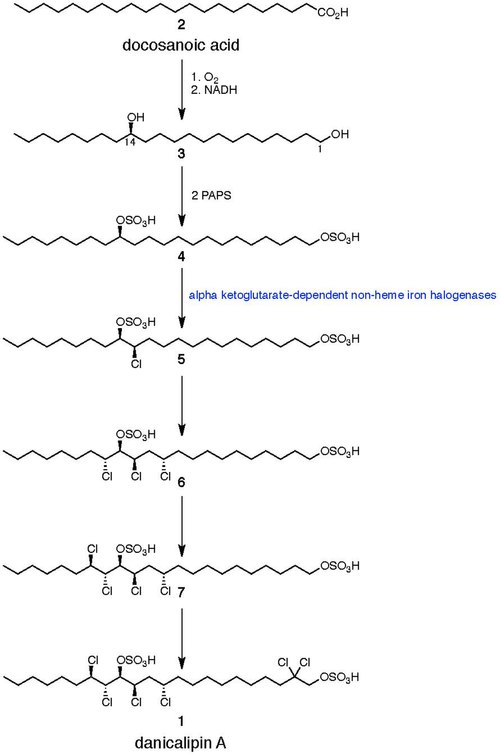
Chlorosulfolipids possess a distinctive structure that sets them apart from other lipid-based molecules. Their backbone is a long-chain fatty acid, which is modified by the presence of sulfur and a varying number of chlorine atoms. The chlorination level and pattern on the carbon chain are critical for the molecule's biological activity and are the basis for their classification. The most studied chlorosulfolipids are those with a high degree of chlorination, such as danicalipin A and mytilipin A, which are found in marine algae.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of chlorosulfolipids is a complex process that involves the incorporation of chlorine and sulfur into fatty acid chains. This process is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve enzyme-catalyzed reactions that selectively introduce chlorine atoms into specific positions on the lipid backbone. The biosynthetic pathway is of significant interest, as it represents a rare example of natural organochlorine production, a process more commonly associated with industrial chemical synthesis.
Biological Activity and Applications
Chlorosulfolipids have been studied for their potential biological activities, including antimicrobial, antifungal, and cytotoxic effects. These properties suggest that chlorosulfolipids could have applications in developing new pharmaceuticals or as bioactive agents in agriculture. However, the toxicity of certain chlorosulfolipid compounds to mammals also raises concerns about their safety and environmental impact.
Environmental Presence
Chlorosulfolipids are primarily found in specific types of marine and freshwater algae, where they may play a role in the organism's defense mechanisms against predators or microbial infection. The environmental distribution and ecological roles of these compounds are areas of ongoing research. Understanding how chlorosulfolipids are produced and function in their natural context is crucial for assessing their potential impact on aquatic ecosystems and their suitability for commercial applications.
Research and Future Directions
Research into chlorosulfolipids is focused on elucidating their biosynthetic pathways, understanding their mechanism of action, and exploring their potential applications. Advances in analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, have facilitated the study of these complex molecules. Future research may uncover new chlorosulfolipid compounds with unique properties and expand our understanding of their role in nature and potential uses in technology and medicine.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD