Choking
(Redirected from Choking sensation)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Choking | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Coughing, gagging, wheezing, cyanosis, inability to speak or breathe |
| Complications | Asphyxia, unconsciousness, cardiac arrest |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Until obstruction is relieved |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Foreign body airway obstruction, swelling, trauma |
| Risks | Eating quickly, alcohol intoxication, dental problems, neurological disorders |
| Diagnosis | Clinical evaluation |
| Differential diagnosis | Asthma, anaphylaxis, heart attack |
| Prevention | Chewing food thoroughly, avoiding talking or laughing while eating |
| Treatment | Back blows, abdominal thrusts, chest compressions, emergency tracheotomy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good if treated promptly |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
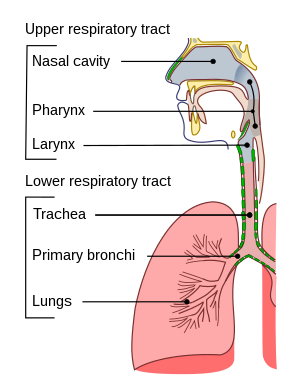
Choking is a blockage of the upper airway which prevents breathing and can be a life-threatening medical emergency. It occurs when a foreign object, often food, gets lodged in the throat or windpipe, blocking the flow of air. In adults, choking most commonly results from food, while in children, small objects are often the cause. Recognizing the signs of choking and knowing how to respond appropriately can be crucial in saving a life.
Signs and Symptoms
The universal sign of choking is clutching the throat with the hand. Other signs include:
- Inability to talk
- Difficulty breathing or noisy breathing
- Sudden cough without an apparent cause
- Skin, lips, and nails turning blue or dusky
- Loss of consciousness if the blockage is not cleared
Causes
Choking can be caused by:
- Eating too quickly, not chewing food well, or talking while eating
- Drinking alcohol before or during meals
- Walking, playing, or running with food or objects in the mouth
- Dentures that do not fit properly, making it difficult to chew food
- Swallowing large pieces of food
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- Chewing food thoroughly and eating slowly
- Avoiding talking or laughing while chewing
- Keeping small objects out of reach of children
- Supervising children while they eat
- Learning the Heimlich maneuver and CPR
First Aid
The Heimlich maneuver is a procedure used to help a choking person:
- Stand behind the person and wrap your arms around their waist.
- Make a fist with one hand and place it just above the person's navel.
- Grasp the fist with the other hand and perform a quick, upward thrust.
- Repeat until the object is expelled.
For infants, a series of back slaps and chest thrusts are recommended.
Treatment
If the choking person becomes unconscious, immediate CPR is necessary. If breathing does not resume after clearing the airway, emergency medical services should be called immediately.
Complications
If not promptly treated, choking can lead to:
- Brain damage due to lack of oxygen
- Death
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD