Cold injury
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Cold injury | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Numbness, tingling, pain, blisters, necrosis |
| Complications | Infection, gangrene, amputation |
| Onset | Exposure to cold temperatures |
| Duration | Varies depending on severity |
| Types | Frostbite, frostnip, trench foot, chilblains |
| Causes | Prolonged exposure to cold, wet conditions, wind chill |
| Risks | Hypothermia, peripheral vascular disease, diabetes, alcohol use |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | Appropriate clothing, limiting exposure, staying dry |
| Treatment | Rewarming, pain management, wound care, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on severity and promptness of treatment |
| Frequency | Common in cold climates |
| Deaths | N/A |
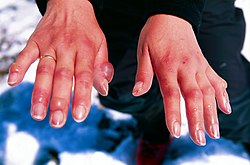
Cold injury refers to damage to skin and underlying tissues caused by extreme cold. It is not to be confused with hypothermia, which is a condition that occurs when your body loses heat faster than it can produce heat.
Types of Cold Injury
There are several types of cold injury, including:
- Frostbite: This is the most common type of cold injury. It occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze. The most susceptible parts of the body are the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks, and chin.
- Frostnip: This is a mild form of frostbite. It usually affects the face, ears, or fingertips.
- Chilblains: These are the painful inflammation of small blood vessels in your skin that occur in response to repeated exposure to cold but not freezing air.
- Trench foot: Also known as immersion foot, it occurs from prolonged exposure to wet and cold conditions. It can occur at temperatures as high as 60 degrees Fahrenheit if the feet are constantly wet.
Causes
Cold injury is caused by exposure to cold, wet, windy conditions. It can occur at any temperature below freezing. The risk of cold injury is increased in people with reduced blood circulation and among people who are not dressed properly for the weather conditions.
Prevention
Prevention of cold injury involves proper preparation for cold weather, including wearing appropriate clothing and ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration.
Treatment
Treatment for cold injuries primarily involves rewarming the affected areas. In severe cases, it may require hospitalization and even amputation.
Cold_injury gallery
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD