Coloboma
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Coloboma | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Vision impairment, photophobia, strabismus |
| Complications | |
| Onset | Congenital |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations, chromosomal abnormalities |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Ophthalmic examination, genetic testing |
| Differential diagnosis | Aniridia, microphthalmia, retinal detachment |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Corrective lenses, surgery |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on severity |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
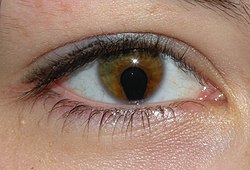
Coloboma refers to a defect in the structure of the eye that is present from birth (congenital). This condition can affect several parts of the eye, including the iris, choroid, eyelid, lens, and optic nerve. Coloboma occurs due to the incomplete closure of the embryonic fissure, a gap in the developing eye, during the fifth to seventh week of pregnancy. The severity and impact of coloboma on vision can vary greatly depending on the size and location of the gap.
Causes
The exact cause of coloboma is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. In some cases, coloboma is associated with genetic syndromes such as CHARGE syndrome, Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13), and Cat Eye syndrome. Genetic mutations affecting eye development can also lead to coloboma when inherited from one or both parents.
Symptoms
Symptoms of coloboma can range from mild to severe and may include:
- A keyhole-shaped pupil if the iris is affected
- Vision loss or impairment, depending on the size and location of the coloboma
- Problems with depth perception
- Increased sensitivity to light
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of coloboma involves a comprehensive eye examination, which may include:
- Visual acuity tests to assess the extent of vision impairment
- Examination of the eye's structure with an ophthalmoscope or slit lamp
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to evaluate the extent of the coloboma and its impact on the eye's structure
Treatment
There is no cure for coloboma, but treatment options are available to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment may include:
- Prescription glasses or contact lenses to improve vision
- Patching the stronger eye to treat or prevent amblyopia in children
- Sunglasses or photochromic lenses to reduce light sensitivity
- Surgery in some cases, such as to repair an eyelid coloboma or to improve the cosmetic appearance of the eye
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with coloboma varies widely and depends on the severity and location of the defect. Some individuals may have minimal vision problems, while others may experience significant vision impairment. Regular eye examinations are important to monitor the condition and manage any complications.
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


