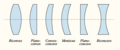
Corrective lens
Corrective lenses are optical devices designed to aid in correcting or improving the vision of individuals with refractive errors, including myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism, and presbyopia. These lenses work by adjusting the direction of light rays to focus precisely on the retina, thereby producing a clearer image.
Types of Corrective Lenses
Corrective lenses come in various forms, each tailored to address specific visual impairments:
- Eyeglasses: The most common type of corrective lens, consisting of a frame holding two lenses adjusted to the wearer's prescription.
- Contact lenses: Thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the eye, offering a more natural field of view and cosmetic appeal.
- Intraocular lenses (IOLs): Surgically implanted lenses within the eye, typically used to replace the eye's natural lens during cataract surgery.
Materials
Corrective lenses can be made from several materials, including:
- Glass: Offers excellent optical clarity but is heavier and more prone to shattering.
- Plastic: Lighter and more impact-resistant than glass, making it a popular choice for everyday wear.
- Polycarbonate: Even lighter and more durable than standard plastic, ideal for children's eyewear and safety glasses.
Lens Treatments
Various treatments can be applied to corrective lenses to enhance their functionality and durability:
- Anti-reflective coating: Reduces glare and reflections, improving visual clarity and comfort.
- UV protection: Blocks harmful ultraviolet rays from reaching the eye, important for outdoor wear.
- Scratch-resistant coating: Helps protect lenses from surface damage, extending their lifespan.
Prescription Process
Obtaining corrective lenses involves a comprehensive eye examination by an optometrist or ophthalmologist. The examination assesses visual acuity, eye health, and the presence of refractive errors. Based on the findings, a prescription is provided, detailing the lens power needed to correct vision.
History
The concept of corrective lenses dates back to ancient times, with the first recorded use of magnifying lenses in the 8th century. The invention of spectacles is attributed to the Italians in the 13th century, with significant advancements in lens technology and design occurring over the centuries.
Future Developments
The field of corrective lenses continues to evolve, with research focused on innovative materials, designs, and technologies. Developments such as customizable contact lenses, lenses capable of adjusting focus electronically, and treatments for preventing or slowing the progression of certain eye conditions are areas of ongoing study.
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD