Cortical deafness
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Cortical deafness | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Inability to hear sounds despite intact ears and auditory pathways |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Sudden or gradual, depending on cause |
| Duration | Permanent |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Bilateral damage to the primary auditory cortex |
| Risks | Stroke, traumatic brain injury, encephalitis |
| Diagnosis | Audiometry, brain imaging |
| Differential diagnosis | Auditory agnosia, pure word deafness, auditory processing disorder |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Rehabilitation, hearing aids |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, often poor |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Cortical deafness is a rare form of hearing loss that occurs due to damage to the primary auditory cortex in the brain. Unlike other forms of hearing impairment, cortical deafness is not caused by damage to the ear or the auditory nerve, but rather by lesions in the cerebral cortex.
Pathophysiology
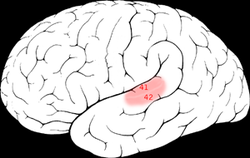
Cortical deafness results from bilateral damage to the primary auditory cortex, which is located in the temporal lobe of the brain. This area is responsible for processing auditory information received from the ears. The primary auditory cortex corresponds to Brodmann areas 41 and 42. Damage to these areas can result from various causes, including stroke, traumatic brain injury, or encephalitis.
Symptoms
Individuals with cortical deafness typically present with a complete inability to perceive sound, despite having intact auditory pathways up to the level of the cortex. This means that the cochlea and auditory nerve are functioning normally, but the brain is unable to interpret the signals. Patients may also experience difficulties with auditory processing and may not respond to auditory stimuli, even though they can hear sounds.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of cortical deafness involves a combination of audiological tests and neuroimaging studies. Audiometry may show normal peripheral hearing function, while MRI or CT scans can reveal lesions in the auditory cortex. Electroencephalography (EEG) may also be used to assess the brain's response to sound.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for cortical deafness, but management focuses on rehabilitation and compensatory strategies. Speech therapy and auditory training may help patients improve their communication skills. In some cases, assistive listening devices or cochlear implants may be used to enhance auditory perception, although their effectiveness can be limited by the cortical damage.
See also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

