Deoxy sugar
Deoxy sugar refers to a type of sugar molecule from which one oxygen atom has been removed. This modification can occur naturally or be induced synthetically, leading to a variety of sugars with distinct properties and biological roles. Deoxy sugars are important in the structure of many biomolecules, including antibiotics, vitamins, and nucleic acids, making them significant in both biochemistry and pharmacology.
Structure and Classification
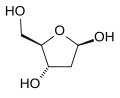
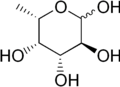
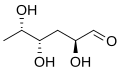
Deoxy sugars retain the general structure of sugars but lack an oxygen atom at one or more positions. This absence significantly alters their chemical reactivity and biological function. They are classified based on the number of carbon atoms (e.g., pentose, hexose) and the position of the deoxy modification. For example, 2-deoxyribose, a component of DNA, is a pentose sugar missing an oxygen atom at the second carbon.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of deoxy sugars involves enzymatic reactions that remove oxygen atoms from sugar precursors. These reactions are catalyzed by enzymes known as dehydratases or reductases. The specific pathways and enzymes involved vary depending on the type of deoxy sugar being synthesized and its biological source.
Biological Role
Deoxy sugars play crucial roles in various biological processes. For instance, 2-deoxyribose is essential for the structure of DNA, where it forms part of the backbone linking nucleotides. Other deoxy sugars are components of antibiotics, such as erythromycin, where they contribute to the molecule's ability to inhibit bacterial growth.
Synthetic Applications
In addition to their natural occurrence, deoxy sugars are synthesized for use in research and drug development. Synthetic deoxy sugars can serve as building blocks for complex molecules, including potential new drugs. Their modified properties compared to regular sugars make them valuable tools in organic chemistry and medicinal chemistry.
Health Implications
The study of deoxy sugars and their derivatives has implications for understanding and treating various diseases. For example, certain deoxy sugar derivatives are being explored for their potential as antiviral or anticancer agents. Understanding the role of natural deoxy sugars in biological systems can also lead to insights into genetic disorders and metabolic diseases.
See Also
This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Deoxy_sugar
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD