Electron therapy
Electron therapy is a type of radiation therapy that uses electrons to treat superficial tumors. It is a form of external beam radiation therapy that is particularly effective for treating skin cancer, lymph nodes, and tumors that are near the surface of the body.
Principles of Electron Therapy
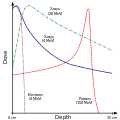
Electron therapy utilizes high-energy electrons, typically in the range of 6 to 20 MeV, to deliver radiation doses to the target tissue. The unique characteristic of electrons is their ability to deposit energy at a specific depth, which is determined by their initial energy. This property allows for the sparing of deeper tissues, making electron therapy ideal for treating superficial lesions.
The dose distribution of electron beams is characterized by a rapid dose fall-off beyond the target depth, as illustrated in the dose depth curves. This feature minimizes the exposure of underlying healthy tissues to radiation, reducing potential side effects.
Applications
Electron therapy is commonly used in the treatment of:
- Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
- Keloids
- Mycosis fungoides
- Breast cancer post-mastectomy chest wall irradiation
- Lymphoma
Advantages and Limitations
The primary advantage of electron therapy is its ability to deliver a high dose to superficial tumors while sparing deeper tissues. This makes it particularly useful for treating cancers that are located close to the skin surface.
However, electron therapy has limitations, including:
- Limited penetration depth, making it unsuitable for deep-seated tumors
- Difficulty in treating irregularly shaped tumors due to the uniformity of the electron beam
Treatment Planning
Treatment planning for electron therapy involves determining the appropriate energy level and field size to ensure adequate coverage of the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissue. Bolus material may be used to bring the dose closer to the skin surface or to compensate for tissue irregularities.
Equipment
Electron therapy is delivered using a linear accelerator (linac), which accelerates electrons to the desired energy level. The linac is equipped with a multileaf collimator to shape the beam and a treatment couch to position the patient accurately.
Related Pages
Electron_therapy
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD