Forkhead box protein O1
(Redirected from FOXO1)
Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) is a transcription factor that belongs to the Forkhead box (FOX) family of proteins. It plays a crucial role in the regulation of various cellular processes, including apoptosis, cell cycle control, glucose metabolism, and oxidative stress resistance.
Structure
FOXO1 is characterized by the presence of a conserved Forkhead DNA-binding domain, which allows it to bind to specific DNA sequences and regulate the expression of target genes. The protein also contains several other functional domains, including a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and a nuclear export signal (NES), which regulate its subcellular localization.
Function
FOXO1 is involved in the regulation of a wide range of biological processes:
Apoptosis
FOXO1 promotes apoptosis by upregulating the expression of pro-apoptotic genes such as Bim and FasL. This function is particularly important in the context of cancer, where the loss of FOXO1 activity can contribute to uncontrolled cell proliferation.
Cell Cycle Control
FOXO1 plays a role in cell cycle regulation by inducing the expression of p27^Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that causes cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. This function is critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing tumorigenesis.
Glucose Metabolism
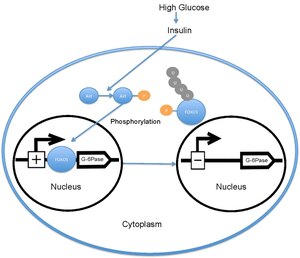
FOXO1 is a key regulator of glucose metabolism. It promotes gluconeogenesis by upregulating the expression of genes such as PEPCK and G6Pase. In the context of insulin signaling, FOXO1 activity is inhibited by Akt-mediated phosphorylation, which leads to its exclusion from the nucleus and subsequent degradation.
Oxidative Stress Resistance
FOXO1 enhances cellular resistance to oxidative stress by inducing the expression of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD2 and catalase. This function is important for protecting cells from damage caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
Regulation
FOXO1 activity is tightly regulated by various post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination. These modifications influence its subcellular localization, stability, and transcriptional activity. For example, phosphorylation by Akt leads to the sequestration of FOXO1 in the cytoplasm, thereby inhibiting its transcriptional activity.
Clinical Significance
Dysregulation of FOXO1 has been implicated in several diseases, including cancer, diabetes mellitus, and neurodegenerative diseases. In cancer, the loss of FOXO1 function can contribute to tumor progression and resistance to therapy. In diabetes mellitus, impaired FOXO1 activity can lead to dysregulated glucose homeostasis.
See Also
References
External Links
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
This transcription-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD