Feliformia
Feliformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora, consisting of "cat-like" carnivorous mammals, including true cats (family Felidae), hyenas (family Hyaenidae), the mongoose (family Herpestidae), and several other less well-known groups. The term "Feliformia" is derived from the Latin "felis" meaning cat and "forma" meaning form or shape, reflecting the shared morphological characteristics that distinguish these animals from other carnivores, known as Caniformia (dog-like carnivores).
Characteristics
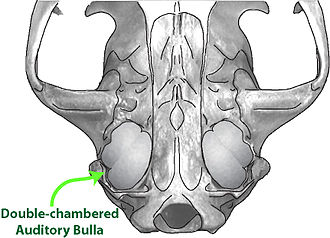
Feliform carnivores are distinguished by several physical characteristics. They typically have a more elongated and flexible body, retractable claws (except in the hyena family where they are non-retractable), and a more highly developed auditory bulla, which is a bony structure enclosing the middle and inner ear. Most feliforms have sharp, conical teeth adapted for a diet primarily consisting of meat. Their cranial structure is also distinct, with a shortened rostrum and a strong emphasis on the development of the facial region, which houses powerful jaw muscles.
Evolution
The evolutionary history of Feliformia dates back to the early Eocene epoch, approximately 55 million years ago. The earliest feliforms were small, arboreal animals, which gradually diversified into a wide range of terrestrial, fossorial (burrowing), and semi-aquatic forms. Over millions of years, feliforms have adapted to various ecological niches, leading to the diversity of species we see today. The split between Feliformia and its sister group, Caniformia, is one of the most significant evolutionary events within the carnivores, highlighting the adaptability and evolutionary success of these mammalian lineages.
Families
Feliformia encompasses several families, each with its unique adaptations and ecological roles. The most well-known family is the Felidae, which includes lions, tigers, leopards, and domestic cats. Other families within Feliformia include:
- Hyaenidae: Comprising hyenas and the aardwolf, known for their strong jaws and scavenging habits. - Herpestidae: The mongoose family, which includes animals known for their agility and ability to hunt venomous snakes. - Viverridae: Including civets and genets, this family is characterized by its diverse range of species that occupy various ecological niches. - Eupleridae: A family of carnivores endemic to Madagascar, including the fossa, which is often mistaken for a large cat.
Conservation
Many feliform species are currently facing threats from habitat loss, poaching, and conflict with humans. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of these unique carnivores. Protected areas, anti-poaching measures, and public education are among the strategies being employed to protect feliform populations.
See Also
- Carnivora - Predation - Conservation biology
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD