Hydrops fetalis
(Redirected from Fetal hydrops)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Hydrops fetalis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Fetal hydrops |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Edema, ascites, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion |
| Complications | Heart failure, fetal death |
| Onset | Prenatal |
| Duration | Varies |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Immune hydrops, non-immune hydrops |
| Risks | Maternal diabetes, parvovirus B19 infection, Rh incompatibility |
| Diagnosis | Ultrasound, amniocentesis, Doppler ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | Congenital heart defect, chromosomal abnormalities |
| Prevention | Rh immunoglobulin, prenatal care |
| Treatment | Intrauterine transfusion, early delivery, supportive care |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Hydrops fetalis is a serious fetal condition defined by an abnormal accumulation of fluid in two or more fetal compartments, including in the subcutaneous tissue, pleura, pericardium, or in the abdomen, which is also known as ascites. Hydrops fetalis can be immune or nonimmune.
Immune Hydrops Fetalis
Immune hydrops fetalis is a complication of a severe form of Rh incompatibility, which can occur when the blood type of a pregnant woman is Rh negative and the blood type of her fetus is Rh positive. This can lead to Rh disease, a condition that occurs when the Rh factors in the mom's blood and baby's blood don't match. It can cause the mother's immune system to react and create antibodies that attack and destroy the baby's red blood cells. This can lead to severe anemia, leading to hydrops fetalis.
Nonimmune Hydrops Fetalis
Nonimmune hydrops fetalis, the more common type, occurs as a result of several diseases, including cardiovascular defects, chromosomal abnormalities, and intrauterine infections.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hydrops fetalis may include:
- Severe swelling in the fetus
- Excessive fluid in the placenta
- Thickened placenta
- Fluid accumulation in the spaces of the baby's body, including the abdomen, pleura, and pericardium.
Diagnosis
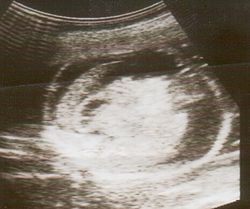
Hydrops fetalis can be diagnosed during pregnancy by using ultrasound imaging. The condition can also be suggested by a polyhydramnios, which is an excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid.
Treatment
The treatment for hydrops fetalis depends on the cause. If it is caused by Rh incompatibility, the mother may receive Rh immune globulin at 28 weeks of gestation and at delivery to prevent her from developing antibodies against her baby's blood cells. Other treatments may include intrauterine fetal blood transfusions and early delivery.
Prognosis
The prognosis for hydrops fetalis depends on the underlying cause. The condition is typically very serious and is often fatal.
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD


