Fuzzy logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of multi-valued logic that deals with reasoning that is approximate rather than fixed and exact. Developed by Lotfi Zadeh in the 1960s, it provides a mathematical strength to the uncertainty and imprecision inherent in many systems. Unlike traditional Boolean logic which operates on binary values (true or false, 0 or 1), fuzzy logic works with degrees of truth or the probability of an event occurring, which are expressed in values between 0 and 1. This approach is particularly useful in fields such as artificial intelligence, control systems, and decision-making processes where binary logic fails to accurately describe real-world scenarios.
Overview
Fuzzy logic is based on the idea that all things admit of degrees. For example, while a traditional logic might require that a statement like "John is tall" be either completely true or completely false, fuzzy logic allows for the possibility that the statement can be partly true to some degree. In this way, fuzzy logic can handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completely false.
Principles
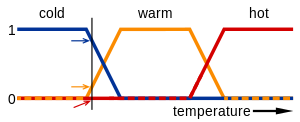
The core of fuzzy logic is the concept of a fuzzy set, which is a generalization of the classical notion of a set. In a fuzzy set, each element has a degree of membership ranging from 0 to 1. A key principle in fuzzy logic is the use of linguistic variables, which are variables whose values are words or sentences rather than numeric values. These words or sentences are often defined by fuzzy sets. For example, temperatures can be described as "high", "medium", or "low", with each term defined by a fuzzy set on the temperature scale.
Applications
Fuzzy logic has been applied in various domains, including:
- Control systems: Fuzzy logic controllers are used in automotive systems, home appliances, and industrial controls where they manage conditions that are difficult to define precisely. - Artificial intelligence: It is used in natural language processing, expert systems, and other areas where decision-making involves uncertainty or imprecision. - Decision-making: Fuzzy logic aids in making decisions based on imprecise or incomplete information, making it valuable in fields like economics and management.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantage of fuzzy logic is its ability to model uncertain or ambiguous data in a way that is closer to how humans make decisions. However, one of the criticisms of fuzzy logic is that it can be more computationally intensive than traditional binary logic, and its mathematical foundations can be less intuitive.
Conclusion
Fuzzy logic offers a valuable framework for dealing with the complexity and ambiguity of the real world. By allowing for degrees of truth and the representation of uncertainty, it provides a more nuanced approach to reasoning and decision-making than traditional binary logic.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD