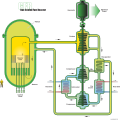
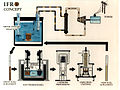
Generation IV reactor
Generation IV reactor is a type of nuclear reactor that is currently in the research and development phase. These reactors are part of the Generation IV International Forum (GIF) initiative, which aims to develop new nuclear technologies that can meet future energy demands while addressing concerns about nuclear waste, safety, proliferation, and cost.
History
The concept of Generation IV reactors was first proposed in the late 1990s by the United States Department of Energy (DOE). In 2000, the DOE established the Generation IV International Forum (GIF), a multinational initiative to collaborate on the research and development of advanced nuclear technologies. The GIF currently includes 14 member countries, including the United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, and several European countries.
Design and Technology
Generation IV reactors are designed to improve upon the technologies used in Generation III and Generation III+ reactors, which are the most advanced reactors currently in operation. The main goals of Generation IV reactor designs are to increase safety, reduce waste, prevent proliferation, and improve cost-effectiveness.
There are six reactor technologies currently being researched and developed under the GIF initiative:
- Gas-cooled fast reactor (GFR)
- Lead-cooled fast reactor (LFR)
- Molten salt reactor (MSR)
- Supercritical water-cooled reactor (SCWR)
- Sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR)
- Very high temperature reactor (VHTR)
Each of these technologies has its own unique advantages and challenges, and they are all at different stages of development.
Future Prospects
While Generation IV reactors hold great promise for the future of nuclear energy, they are still in the research and development phase and it is likely to be several decades before they are commercially viable. However, the GIF continues to make progress in advancing these technologies, and several member countries have announced plans to build prototype Generation IV reactors in the coming years.
See Also
References
This article is a nuclear physics or atomic physics–related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD