Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Marconi (25 April 1874 – 20 July 1937) was an Italian inventor and electrical engineer known for his pioneering work on long-distance radio transmission and for his development of Marconi's law and a radio telegraph system. He is often credited as the inventor of radio, and he shared the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy". Marconi's work in radio transmission has made him one of the most celebrated figures in the history of technology.
Early Life
Guglielmo Marconi was born in Bologna, Italy, into a wealthy family. His father was Italian and his mother was Irish. From a young age, Marconi was fascinated by science and technology, particularly the work of Heinrich Hertz in electromagnetic radiation. Marconi's education was a mix of private tutoring and formal schooling in Bologna and Florence.
Inventions and Discoveries
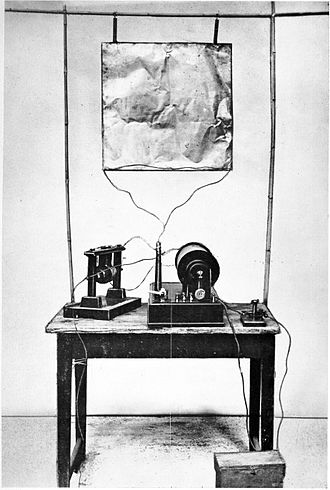
In 1895, Marconi began experimenting with wireless telegraphy. His early experiments were based on the use of Hertzian waves (radio waves) to transmit Morse code signals over distances without wires. By 1896, he had successfully sent signals over a distance of about 2 miles. This success led him to patent his system and establish the Marconi Company to develop and market his technology.
Marconi's work progressed rapidly, and in 1901, he achieved the first successful transatlantic wireless telegraphy transmission between Cornwall, England, and Newfoundland, Canada. This historic event demonstrated the potential of wireless communication over long distances and marked a significant milestone in the development of modern radio.
Throughout his career, Marconi continued to innovate and improve wireless technology. He introduced the concept of using short waves for long-distance communication, which greatly enhanced the capabilities of radio transmission. Marconi's contributions to radio technology were fundamental to the development of modern communication systems.
Later Life and Legacy
Marconi continued to work on perfecting radio technology until his death in 1937. Over his lifetime, he received numerous awards and recognitions for his contributions to science and technology, including the Nobel Prize in Physics.
Today, Marconi is remembered as a pioneer of wireless communication. His work laid the foundation for the development of radio, television, and later, the internet. The impact of his inventions on communication and information sharing cannot be overstated, making him one of the key figures in the technological revolution of the 20th century.
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD