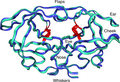
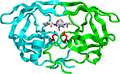
HIV-1 protease
HIV-1 protease is an enzyme that plays a critical role in the life cycle of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1), which is the virus responsible for the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). This enzyme is essential for the post-translational processing of the viral polyproteins, leading to the maturation of the virus and its ability to infect new cells. Due to its crucial role in the viral life cycle, HIV-1 protease has been a prime target for antiretroviral therapy aimed at treating HIV/AIDS.
Function
HIV-1 protease is a dimer, consisting of two identical subunits, each comprising 99 amino acids. It cleaves the Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins at specific sites, leading to the structural proteins and enzymes necessary for the assembly of new virions. Without the activity of HIV-1 protease, the viral particles remain immature and non-infectious.
Structure
The enzyme's active site is located in a cleft between the two subunits, and it has a unique Aspartyl protease mechanism, utilizing two aspartate residues to cleave the peptide bond. The specificity of HIV-1 protease for its substrates is highly precise, making it an attractive target for drug design.
Inhibition and Drug Resistance
The inhibition of HIV-1 protease disrupts the viral replication cycle, making protease inhibitors (PIs) a key component of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART). However, the high mutation rate of HIV-1 leads to the emergence of drug-resistant strains, posing significant challenges to the effectiveness of PIs. Continuous efforts in drug development are necessary to overcome resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
Clinical Significance
The discovery of HIV-1 protease and its role in the viral life cycle has had a profound impact on the management of HIV/AIDS. Protease inhibitors have significantly improved the life expectancy and quality of life for individuals living with HIV. Ongoing research focuses on developing new inhibitors with better efficacy and resistance profiles, as well as understanding the mechanisms of drug resistance.
See Also
HIV-1_protease
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD