Acute interstitial pneumonitis
(Redirected from Hamman–Rich syndrome)
| Acute interstitial pneumonitis | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Hamman–Rich syndrome |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
| Symptoms | Cough, dyspnea, fever |
| Complications | Respiratory failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Days to weeks |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Unknown, possibly viral infection or autoimmune disease |
| Risks | Smoking, viral infections, autoimmune disorders |
| Diagnosis | Chest X-ray, CT scan, lung biopsy |
| Differential diagnosis | Acute respiratory distress syndrome, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Supportive care, mechanical ventilation, corticosteroids |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Poor, high mortality rate |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Acute interstitial pneumonitis
Acute interstitial pneumonitis (AIP), also known as Hamman-Rich syndrome, is a rare and severe form of interstitial lung disease characterized by the rapid onset of respiratory failure. It is classified as an idiopathic form of diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) and is considered a type of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Pathophysiology
AIP is characterized by diffuse alveolar damage, which involves injury to the alveolar epithelium and capillary endothelium. This leads to the formation of hyaline membranes, interstitial edema, and infiltration of inflammatory cells. The exact cause of AIP is unknown, but it is thought to be triggered by an acute inflammatory response in the lungs.
Clinical presentation
Patients with AIP typically present with sudden onset of dyspnea, cough, and fever. The condition progresses rapidly to severe respiratory failure, often requiring mechanical ventilation. The clinical course is similar to that of ARDS, but AIP is distinguished by its idiopathic nature and histological findings.
Diagnosis
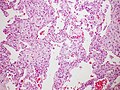
The diagnosis of AIP is based on clinical presentation, imaging studies, and histopathological examination. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the chest often shows diffuse bilateral ground-glass opacities and consolidation. A lung biopsy is usually required to confirm the diagnosis, revealing the characteristic diffuse alveolar damage with hyaline membrane formation.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for AIP, and management is primarily supportive. Patients often require mechanical ventilation and intensive care. Corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive agents may be used, but their efficacy is uncertain. The prognosis is generally poor, with a high mortality rate.
Prognosis
The prognosis of AIP is poor, with a high mortality rate, often exceeding 50%. Survivors may experience long-term pulmonary sequelae, including pulmonary fibrosis.
Related pages
- Interstitial lung disease
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Diffuse alveolar damage
- Pulmonary fibrosis
Gallery
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD