Hellenistic period
(Redirected from Hellenistic)
Hellenistic period
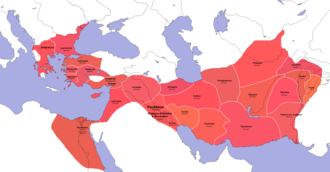
The Hellenistic period covers the era from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC to the emergence of the Roman Empire as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the subsequent conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. This epoch is characterized by the expansion of Greek culture across the Mediterranean and into the Near East and Asia, through the networks of trade and the conquests initiated by Alexander and continued by his successors, the Diadochi.
Origins and Historical Overview
Following the death of Alexander the Great, his empire was divided among his generals, leading to the formation of several Hellenistic kingdoms. The most prominent of these were the Seleucid Empire, the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt, the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, and the Indo-Greek Kingdom. These states were characterized by new levels of cultural and political interaction between the Greek and local populations.
Culture and Society
The Hellenistic period was marked by significant cultural developments, including advances in science, philosophy, literature, and the arts. The Library of Alexandria in Egypt became a center for learning, housing texts from all over the known world. In philosophy, schools such as the Stoics, the Epicureans, and the Skeptics emerged, reflecting the diverse intellectual landscape of the time.
Art and Architecture
Hellenistic art and architecture spread throughout the empire, characterized by its realism, as seen in sculptures such as the Venus de Milo and the Laocoön Group. New architectural styles and innovations, including the use of the Corinthian order, became widespread.
Economy
The Hellenistic period saw the expansion of trade networks that connected the Mediterranean with the East, facilitating the exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas. The economy was marked by the increased use of coinage, the growth of cities, and the rise of a merchant class.
Military and Warfare
The era was also defined by its military innovations, including the use of war elephants and the development of new siege technologies. The Diadochi wars, a series of conflicts among Alexander's successors, were a significant feature of the period, leading to the eventual dominance of the Hellenistic kingdoms by Rome.
End of the Hellenistic Period
The Hellenistic period came to a close with the Roman conquest of the Greek world, culminating in the fall of Alexandria in 30 BC. Despite the end of Hellenistic political sovereignty, the cultural and intellectual legacy of the Hellenistic world continued to influence the Roman Empire and beyond.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD