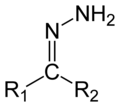
Hydrazone
Hydrazone refers to a class of organic compounds characterized by the functional group R1R2C=NNH2, where R1 and R2 can be carbon or hydrogen atoms. Hydrazones are formed by the reaction of hydrazines with ketones or aldehydes. This reaction is an important tool in organic synthesis and analytical chemistry, particularly in the identification and characterization of various carbonyl compounds.
Formation
The formation of hydrazones involves the nucleophilic addition of a hydrazine to the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction typically occurs under mild conditions, often simply by mixing the reactants in the presence of an acid or base catalyst. The general equation for the formation of a hydrazone is as follows:
R2C=O + N2H4 → R2C=NNH2 + H2O
where R2C=O represents a ketone or aldehyde, and N2H4 is hydrazine.
Properties
Hydrazones are known for their varied chemical properties, which depend on the nature of the substituents R1 and R2. They can exhibit different degrees of stability, reactivity, and solubility in various solvents. Some hydrazones are crystalline solids at room temperature, making them useful for the purification and isolation of specific compounds through crystallization.
Applications
Hydrazones find applications in several areas of chemistry:
- Organic Synthesis: They are intermediates in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Hydrazones can undergo further chemical transformations, such as the Wolff-Kishner reduction, to produce amines or alkenes.
- Analytical Chemistry: Hydrazones are employed in the qualitative and quantitative analysis of carbonyl compounds. Their formation is a basis for various colorimetric assays and spectrophotometric methods used to detect and measure aldehydes and ketones.
- Pharmaceuticals: Certain hydrazone derivatives exhibit biological activity and are investigated for their therapeutic potential. They have been studied as antimicrobial, antiviral, and anticancer agents.
Chemical Reactions
Hydrazones participate in several chemical reactions, including:
- Wolff-Kishner Reduction: A method for converting hydrazones into alkanes.
- Bamford-Stevens Reaction: A process that transforms tosylhydrazone derivatives into alkenes or alkynes under thermal or photolytic conditions.
- Hydrazone Iodination: A reaction that involves the iodination of hydrazones to form iodohydrins.
Safety and Handling
Hydrazones should be handled with care, as some derivatives can be hazardous. Proper safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and adequate ventilation, are essential when working with these compounds.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD