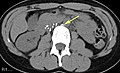
Inferior vena cava filter
Inferior Vena Cava Filter
The inferior vena cava filter (IVC filter) is a type of vascular filter that is implanted by interventional radiologists or vascular surgeons into the inferior vena cava to prevent pulmonary embolism (PE). Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs usually caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs or, rarely, other parts of the body (deep vein thrombosis). Because the inferior vena cava is the main vessel returning blood from the lower half of the body to the heart, placing a filter in this location can catch emboli before they enter the lungs.
Indications
The primary indication for the placement of an IVC filter is to provide protection against pulmonary embolism in patients who are at high risk for such events and in whom anticoagulant therapy is contraindicated, has failed, or is not tolerated. This includes patients with:
- Recurrent PE despite adequate anticoagulation
- Contraindication to anticoagulation (e.g., recent surgery, bleeding disorders)
- Complications from anticoagulation
- Massive PE with residual deep vein thrombosis in patients who cannot receive anticoagulation
Types of Filters
There are several types of IVC filters, including permanent and retrievable filters. Retrievable filters are designed to be removed once the risk of PE has subsided. However, not all retrievable filters are removed, and the decision to remove a filter is based on the patient's risk of PE versus the risk of having the filter in place.
Procedure
The insertion of an IVC filter is typically performed under local anesthesia and sedation. Using fluoroscopic guidance, the filter is inserted through a catheter that is placed into a vein in the neck or groin and advanced to the inferior vena cava. Once in the correct position, the filter is deployed from the catheter and placed in the inferior vena cava.
Risks and Complications
While the placement of an IVC filter can be life-saving for patients at risk of PE, there are associated risks and complications, including:
- Filter migration
- Filter fracture
- IVC perforation
- Deep vein thrombosis at the insertion site
- Difficulty removing the filter
Follow-up
Patients with an IVC filter require regular follow-up to assess the filter's position, integrity, and the ongoing risk of PE. This may include imaging studies such as duplex ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
Conclusion
The use of inferior vena cava filters is a critical intervention in the prevention of pulmonary embolism in patients who cannot be managed with anticoagulation therapy alone. While effective, the decision to place an IVC filter must be carefully considered against the potential risks and complications associated with the device.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD