Interventricular foramina (neuroanatomy)
Interventricular Foramina (Neuroanatomy)
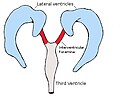
The interventricular foramina, also known as the foramina of Monro, are small openings that connect the lateral ventricles of the brain with the third ventricle. These foramina play a crucial role in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain.
Anatomy
The interventricular foramina are located in the midline of the brain, connecting the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle. Each foramen is situated between the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle and the anterior end of the third ventricle. They are named after Alexander Monro, a Scottish anatomist who first described them in the 18th century.
The foramina are approximately 1-2 mm in diameter and are surrounded by a ring of tissue known as the choroid plexus. The choroid plexus is responsible for the production of CSF, which fills the ventricles and provides cushioning and support to the brain.
Function
The interventricular foramina serve as channels for the flow of CSF between the lateral ventricles and the third ventricle. CSF is produced by the choroid plexus within the lateral ventricles and needs to circulate throughout the ventricular system to maintain a stable environment for the brain.
CSF flows from the lateral ventricles into the third ventricle through the interventricular foramina. From the third ventricle, it continues its circulation through the cerebral aqueduct, which connects the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle. Finally, CSF exits the fourth ventricle and enters the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
Clinical Significance
The interventricular foramina can be affected by various pathological conditions, leading to disruptions in CSF circulation. One such condition is hydrocephalus, which is characterized by an abnormal accumulation of CSF within the ventricles. This can occur due to blockage or narrowing of the interventricular foramina, preventing the normal flow of CSF.
In cases of hydrocephalus, increased pressure within the ventricles can cause symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and changes in mental status. Treatment options may include surgical intervention to bypass the obstruction or the placement of a shunt to redirect the excess CSF to another part of the body.
Conclusion
The interventricular foramina are essential structures in the neuroanatomy of the brain. They provide a pathway for the circulation of CSF between the lateral ventricles and the third ventricle. Understanding the anatomy and function of these foramina is crucial in diagnosing and managing conditions that affect CSF circulation, such as hydrocephalus.
For more information on related topics, you can visit the following links: - Lateral ventricles (neuroanatomy) - Third ventricle (neuroanatomy) - Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) - Hydrocephalus
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD