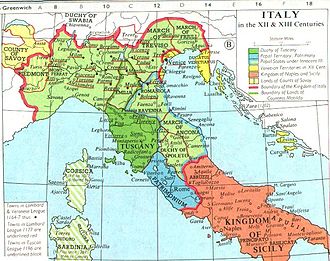
Italy in the Middle Ages
== Italy in the Middle Ages ==
Italy in the Middle Ages refers to the history and development of the Italian peninsula from the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century to the beginning of the Renaissance in the 14th century. This period was marked by significant political, social, and cultural changes.
Early Middle Ages
The early Middle Ages in Italy began with the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD, leading to the establishment of various Germanic kingdoms. The most notable of these were the Ostrogoths, who ruled Italy under Theodoric the Great from 493 to 526 AD. The Ostrogothic Kingdom was eventually overthrown by the Byzantine Empire during the Gothic War (535–554).
Lombard Rule
Following the Gothic War, the Lombards invaded Italy in 568 AD, establishing the Kingdom of the Lombards. Their rule lasted until 774 AD when the kingdom was conquered by the Franks under Charlemagne, who incorporated it into the Carolingian Empire.
The Rise of the Papal States
During the early Middle Ages, the Papal States emerged as a significant political entity. The Donation of Pepin in 756 AD granted the Pope control over a large territory in central Italy, which became the foundation of the Papal States. This period also saw the increasing influence of the Catholic Church in Italian politics and society.
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages in Italy were characterized by the rise of powerful city-states and maritime republics. Notable among these were Venice, Genoa, Pisa, and Amalfi. These city-states became centers of trade, commerce, and culture, playing a crucial role in the economic and cultural development of Europe.
The Norman Conquest of Southern Italy
In the 11th century, the Normans began their conquest of southern Italy, eventually establishing the Kingdom of Sicily in 1130. This kingdom included not only the island of Sicily but also large parts of the southern Italian mainland.
The Holy Roman Empire and the Italian City-States
The relationship between the Holy Roman Empire and the Italian city-states was complex and often contentious. The Investiture Controversy and the subsequent conflicts between the Guelphs and Ghibellines were significant events that shaped the political landscape of Italy during the High Middle Ages.
Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages in Italy saw the decline of feudalism and the rise of powerful city-states such as Florence, Milan, and Venice. This period also witnessed the beginning of the Renaissance, a cultural movement that would have a profound impact on the history of Italy and Europe.
Related Pages
- History of Italy
- Medieval Europe
- Renaissance
- Holy Roman Empire
- Papal States
- Norman Conquest of Southern Italy
- Guelphs and Ghibellines
- Kingdom of the Lombards
- Ostrogothic Kingdom
| History of Italy |
|---|
 |
|
|
This article is a European history–related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD