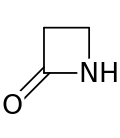
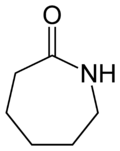
Lactam
Lactams are a class of organic compounds characterized by a carbon-nitrogen bond forming part of a ring structure that includes at least one other carbon atom. The ring can vary in size, and the lactams are named according to the number of carbon atoms in the ring: four-membered lactams are known as β-lactams, five-membered lactams as γ-lactams, six-membered lactams as δ-lactams, and so on, with the Greek letter indicating the position of the nitrogen atom relative to the carbonyl group. Lactams are a crucial structural component in many biologically active compounds and pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics such as the penicillins and cephalosporins, which are β-lactams.
Structure and Nomenclature
The structure of lactams consists of an amide group (a carbonyl group linked to a nitrogen atom) integrated into a cyclic structure. The simplest lactam, β-lactam, has a four-membered ring, making it one of the most strained and reactive lactams. This strain is due to the angle strain and torsional strain on the bonds, which deviates significantly from the ideal tetrahedral geometry of sp^3 hybridized carbon atoms.
Lactams are named by replacing the -oic acid or -ic acid suffix of the corresponding carboxylic acids with -lactam. For example, the lactam derived from butyric acid (butanoic acid) is called butyrolactam (a γ-lactam).
Synthesis
Lactams can be synthesized through several methods, including:
- Direct cycloaddition of amines to ketenes to form β-lactams.
- Cyclization of amino acids or their derivatives, which can lead to various sizes of lactam rings.
- Beckmann rearrangement, where ketoximes are converted to lactams in the presence of acid or base catalysts.
Biological Significance and Applications
Lactams are found in a variety of biologically active molecules. The most well-known lactams are β-lactams, which are used as antibiotics due to their ability to inhibit the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. This class includes penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems. These antibiotics are crucial in the treatment of bacterial infections, and their discovery and development have been a significant milestone in medical history.
Lactams also play a role in the synthesis of synthetic polymers, where they can be used as monomers to create polyamides, which are materials with plastic-like properties.
Resistance and Challenges
The widespread use of β-lactam antibiotics has led to the emergence of resistant bacterial strains. Mechanisms of resistance include the production of β-lactamase enzymes, which hydrolyze the lactam ring, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. This has led to the development of β-lactamase inhibitors, such as clavulanic acid, which are often co-administered with β-lactam antibiotics to combat resistance.
See Also
References
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD